101 Remember Structural Organization Biology Diagrams A tissue membrane is a thin layer or sheet of cells that covers the outside of the body (for example, skin), the organs (for example, pericardium), internal passageways that lead to the exterior of the body (for example, abdominal mesenteries), and the lining of the moveable joint cavities. There are two basic types of tissue membranes Connective tissue is diverse collection of tissues that support and connect other tissues, but also have protective functions. A main feature of connective tissue is that they contain a matrix that gives the tissue it's density. Some bones - like our rib cage - protect delicate organs and. Specialized cells in connective tissue defend the body from microorganisms that enter the body
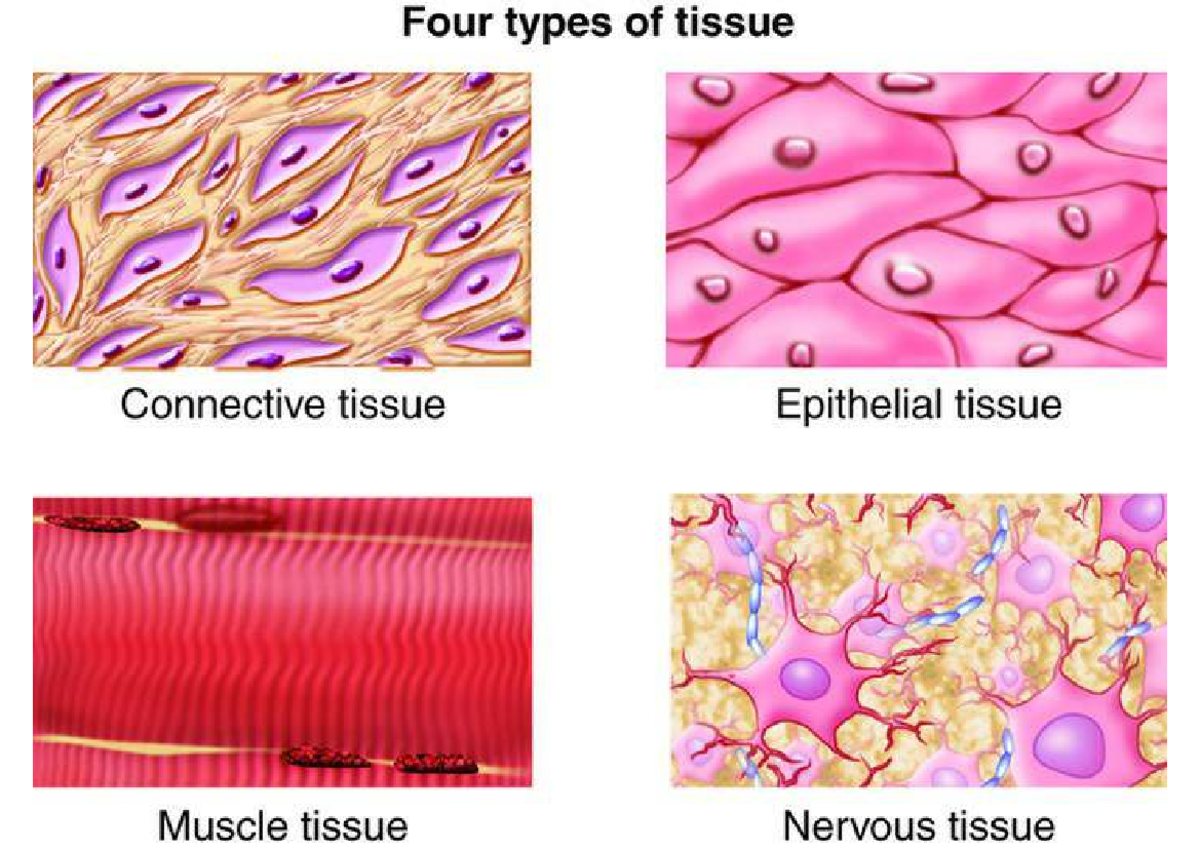
4.1 Types of Tissues. The human body contains more than 200 types of cells that can all be classified into four types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. The structure of a tissue usually is optimized for its function. Describe how the structure of the mucosa and its cells match its function of nutrient absorption. The human body has four main categories of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscular and neural tissues. The branch of biology that studies the microscopic structure of tissues is called histology. Compact bone, x.s. 400x Learning Outcomes. List the 4 main types and characteristics of tissue found in the human body Identify the 4 broad tissue types of the human body; Understand the relationship between structure and function regarding all four tissue types; Although these cells may not play an important role in forming the structure of connective tissue they help maintain the viability of the tissue. The properties of these cells are discussed below.

Chapter 8. Tissue Structure and Functions Biology Diagrams
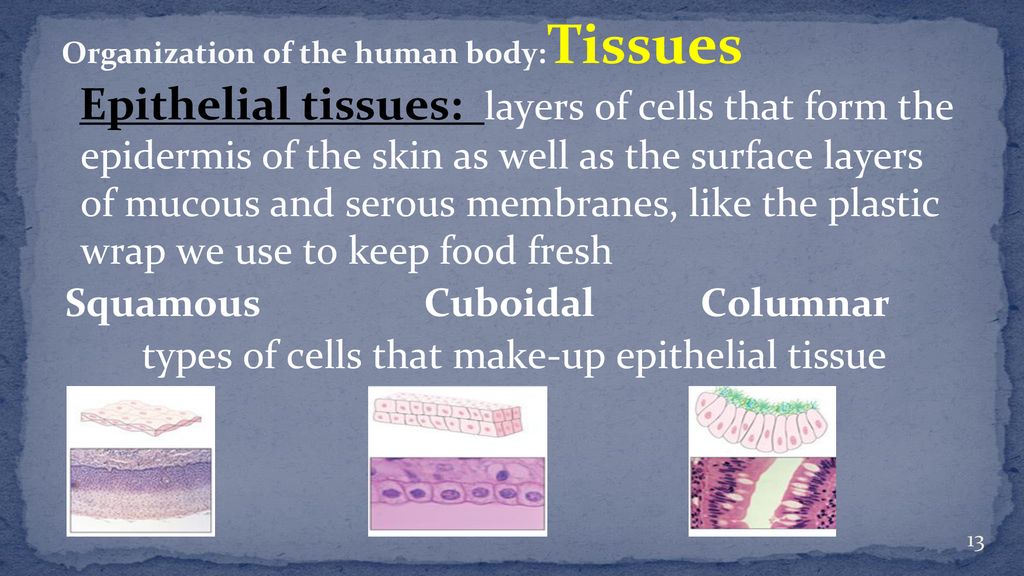
Epithelial cells nuclei (histological slide) Epithelial tissue is a highly cellular tissue that overlies body surfaces, lines cavities, and forms glands.In addition, specialized epithelial cells function as receptors for special senses (smell, taste, hearing, and vision).Epithelial cells are numerous, exist in close apposition to each other, and form specialized junctions to create a barrier
Tissues are the foundation of the human body, consisting of groups of cells that work together to perform specific functions.[6] They form the basis for organs and systems, enabling the body to carry out complex tasks necessary for survival. Understanding the structure, types, and roles of tissues is critical in the study of anatomy and
Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology Biology Diagrams
Tissue Membranes. A tissue membrane is a thin layer or sheet of cells that either covers the outside of the body (e.g., skin), lines an internal body cavity (e.g., peritoneal cavity), lines a vessel (e.g., blood vessel), or lines a movable joint cavity (e.g., synovial joint). Two basic types of tissue membranes are recognized based on the primary tissue type composing each: connective tissue Tissues are groups of cells that have a similar structure and act together to perform a specific function. The word tissue comes from a form of an old French verb meaning "to weave". There are four different types of tissues in animals: connective, muscle, nervous, and epithelial. In plants, tissues are divided into three types: vascular, ground, and epidermal. Groups of tissues make up Dense connective tissue is reinforced by bundles of fibers that provide tensile strength, elasticity, and protection. In loose connective tissue, the fibers are loosely organized, leaving large spaces in between. Supportive connective tissue—bone and cartilage—provide structure and strength to the body and protect soft tissues.