A molecular toolbox for studying protein degradation in mammalian cells Biology Diagrams Key events in mitosis such as sister chromatid separation and subsequent inactivation of cyclin-dependent kinase 1 are regulated by ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis. These events are mediated by the anaphase-promoting complex (APC), a cell cycle-regulated ubiquitin ligase that assembles multiubiquitin chains on regulatory proteins such as securin and cyclins and thereby targets them for The half-lives of proteins within cells vary widely, from minutes to several days, and differential rates of protein degradation are an important aspect of cell regulation. Many rapidly degraded proteins function as regulatory molecules, such as transcription factors. The entry of all eukaryotic cells into mitosis is controlled in part by

During mitosis, known degradative functions are mainly restricted to UPS, specialized in ubiquitin-triggered protein degradation and presumably faster than lysosome-dependent degradation. Lysosomes are acidic cytosolic vesicles responsible to enzymatically degrade all types of biological material. Imbalances in protein levels will occur particularly in protein complexes where the genes encoding individual components of the complex reside on different chromosomes. These imbalances will disrupt protein homeostasis, increase the workload for chaperones, and overload the protein degradation machinery, resulting in a form of toxicity referred Xkid is a microtubule plus end-directed motor that moves chromosomes away from spindle poles in early mitosis. Xkid degradation, therefore, facilitates the segregation of chromatids toward spindle poles in anaphase. It is conceivable that Emi1/Rca1 has a role in Cdh1 degradation because Emi1 is an F box protein that interacts with SCF
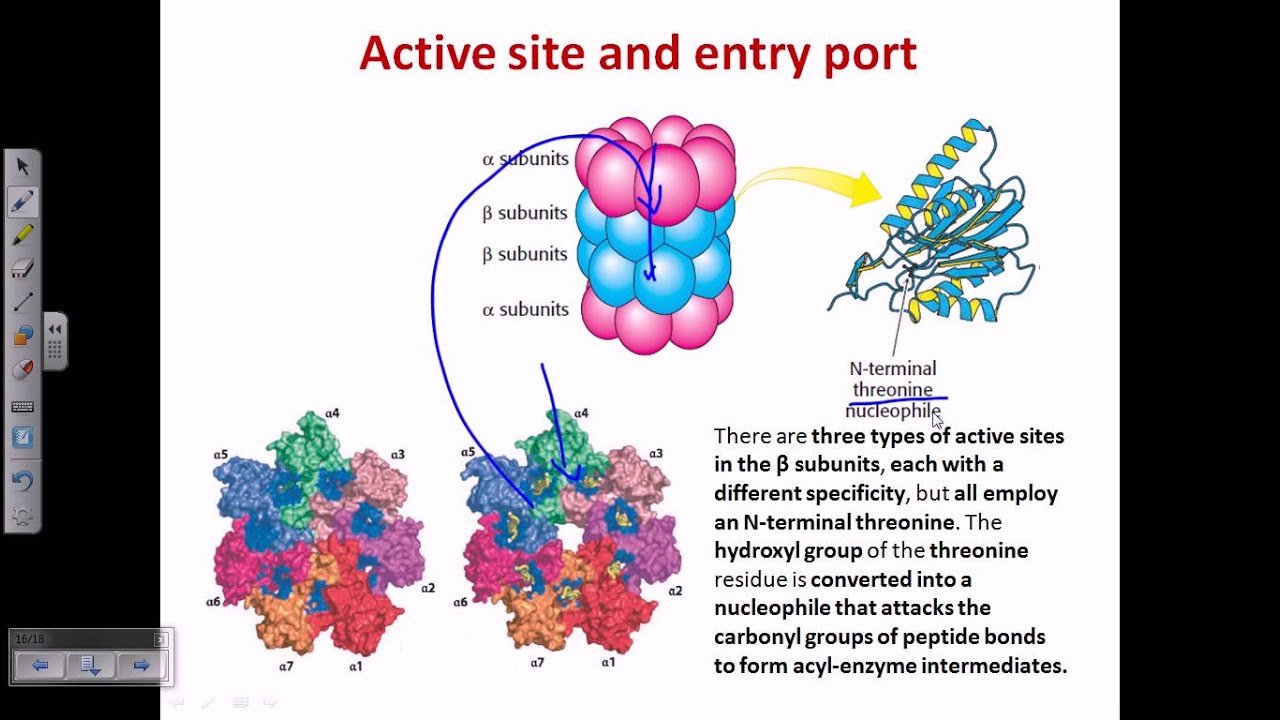
Promoting Complex: Molecular Cell Biology Diagrams
Since the description of mitosis by Flemming in 1882, studies on somatic cell division have focused on the equal partition of cellular materials, in particular that of the chromosomes and mitotic apparatus, between cell daughters (1, 2).We now report that many mitotic divisions are unequal with respect to pericentrosomal proteins targeted for proteasomal degradation.
It has recently become clear that several other proteins are degraded at specific points in mitosis. This review (which is part of the Chromosome Segregation and Aneuploidy series) focuses on how specific proteins are selected for proteolysis at defined points in mitosis and how this contributes to the proper coordination of chromosome Among its many substrates, the APC/C triggers the degradation of proteins that stabilize the mitotic spindle, and loss or accumulation of such spindle assembly factors can result in aneuploidy and cancer. Although critical for cell division, it has remained poorly understood how the timing of spindle assembly factor degradation is established

Mitosis: a matter of getting rid of the right protein at the ... Biology Diagrams
Mouery et al. utilize deep, quantitative proteomics to reveal a PLK1-regulated program of G2/M protein degradation. They show that the PKA-anchoring protein AKAP2 is degraded in a manner dependent on PLK1 and the E3 ubiquitin ligase SCFβTrCP and that disruption of AKAP2 degradation results in defects of the mitotic cytoskeleton.

