A warmer Arctic causes fish to move Biology Diagrams A food chain only shows one direction of how energy is transferred. In nature, it is usually more complex as more than one animal might hunt a specific species. Food Webs The Arctic food web. Click for more detail. When many food chains are linked together they create a food web. Most animals have many food sources and also have many predators.

Polar bears are the top of the Arctic's land-based food chain. Their biggest threat to survival is not other species. Rather it is the changing environmental conditions brought on by climate Christian SaraviaWalruses are some of the most important marine animals and they play a vital role in the health of the arctic and subarctic ecosystems. They are foraging predators who rely heavily on the diverse creatures of the ocean floor. Walruses feed primarily on benthic invertebrates such as clams and mussels. Unfortunately, unsustainable fishing practices disturb the natural balance of and walruses, have a thick layer of blubber (fat) under their skin. Blubber acts like a cozy blanket, keeping the animal warm in freezing water. It also stores energy for when food is hard to find. small body parts Arctic animals often have small ears, tails, and noses to keep from losing heat. Smaller body parts mean less skin is exposed to
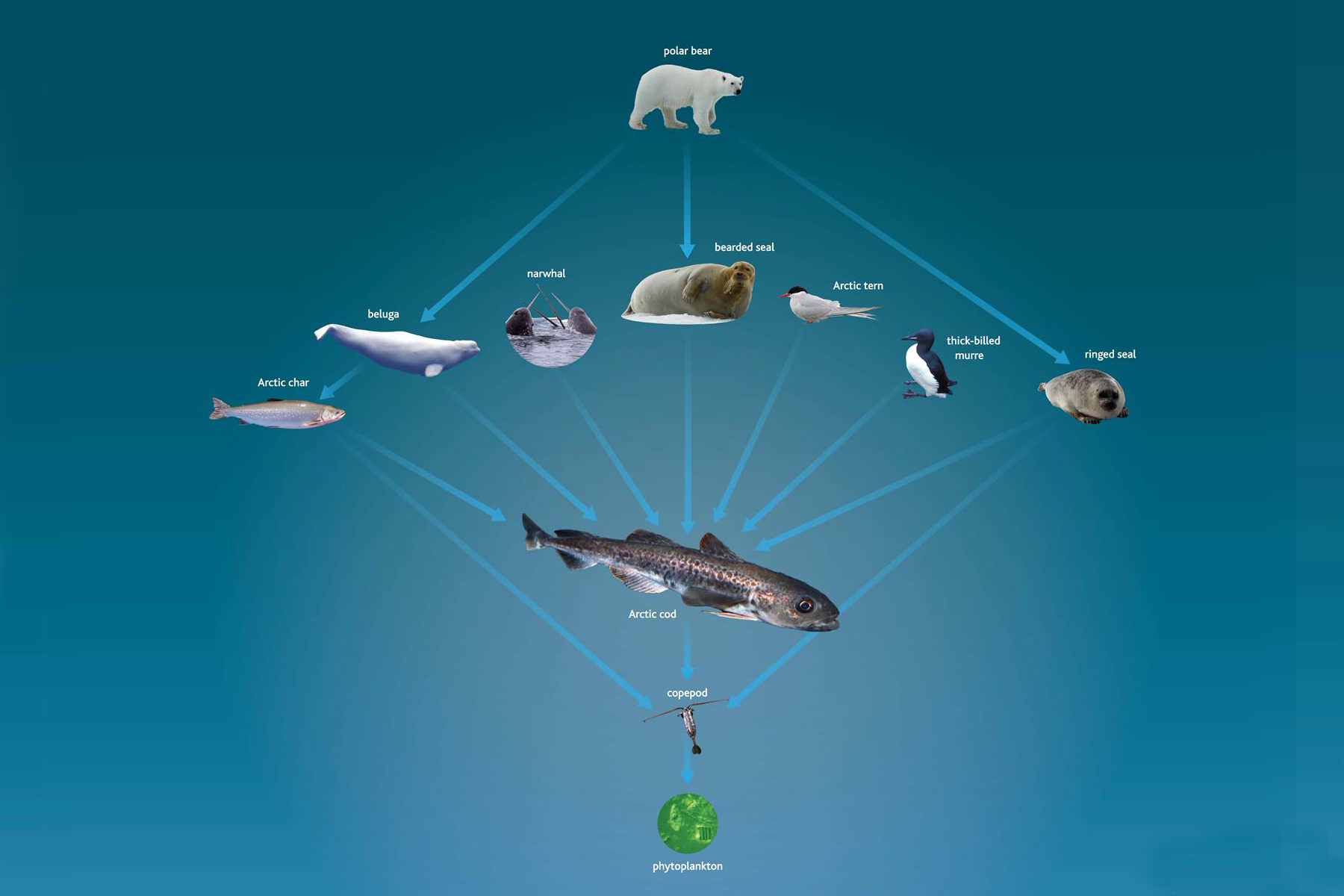
Under the Ice: Understanding the Arctic Food Web Biology Diagrams
Other animals, however, are very dependent on this ice: like polar bears, walruses, and seals, being their resting, breeding, and hunting ground. Scientists say that there are about 240 different species of fish living in the Arctic Ocean. An integral food chain link among them is the Arctic cod, which links the underwater web with the one

Atlantic walruses frequent the coastal areas from northeastern Canada to Greenland, dipping into the waters of the Arctic Ocean. Pacific walruses have a broader range, extending from the Bering Sea to the Chukchi Sea, and occasionally wandering into the Laptev Sea. Contaminants in the water can accumulate in the walrus food chain, affecting Walruses play a significant role in the animal food chain as prey and predators. By feeding on benthic organisms, they influence the structure and the local population of benthic invertebrates. As such, they help maintain a balance in the arctic ecosystem. Further, their foraging behavior makes them the Arctic's keystone species. This particular ice floe, or large piece of floating sea ice, carries a pod of walrus through Arctic waters. Otis is a walrus pup born on that ice floe in late spring in the Chukchi Sea, Ocean acidification is just one way that humans are disrupting the Arctic food chain. Human activity in the Arctic, like oil drilling, can lead to

Arctic Food Web: Everything You Need To Know Biology Diagrams
Food Web on Land Surrounding the Arctic Ocean. Animals like polar bears, walrus, and seals thrive over the Arctic ice and around the snow-capped lands surrounding the area. Polar bears are the apex predator here and comprise the top of the food web. However, they only hunt in the spring, during the summer, and at the start of the autumn season.

