African Savanna Food Chain Biology Diagrams Food chains, or food webs, as they are sometimes called in recognition of their complexity, are part of life in the African savanna, just as they are in every biome on Earth. The African savanna is a mixture of grassland and sparse trees that begins south of the Sahara Desert and stretches to the northern border of As you move up the food chain, each level receives only about 10% of the energy from the level below it. This energy loss limits most food chains to 3-4 trophic levels. Savanna food chains follow these same principles as energy transfers between trophic levels, beginning with producers. Savanna Food Chain Trophic Levels and Components Explained

Africa's grassland, or savanna, ecosystem is an open, grass-covered land with small, interspersed trees. Its diverse species play specific and important roles. Food chains trace the transfer of energy from one organism to another in an ecosystem. They are simple and linear, whereas food webs include all of the The savanna, or African grassland, is a diverse food chain reliant on migration patterns that follow water and food sources. One direct food chain may go as follows: a zebra eats grass and then gets eaten by a lion, which is consumed by vultures and hyenas when it dies. Once the food chain gets to the decomposers, the food chain starts over From the vibrant tapestry of flora to the realm of wildlife, the savanna food web weaves a complex and delicate balance. Grasses, trees, shrubs, and herbs provide nourishment for an array of animals, including antelopes, zebras, giraffes, and elephants. Predators like lions, leopards, and cheetahs hunt these herbivores, shaping the ecosystem's dynamics. Symbiotic relationships between flora

PDF African Savanna Background Information Biology Diagrams
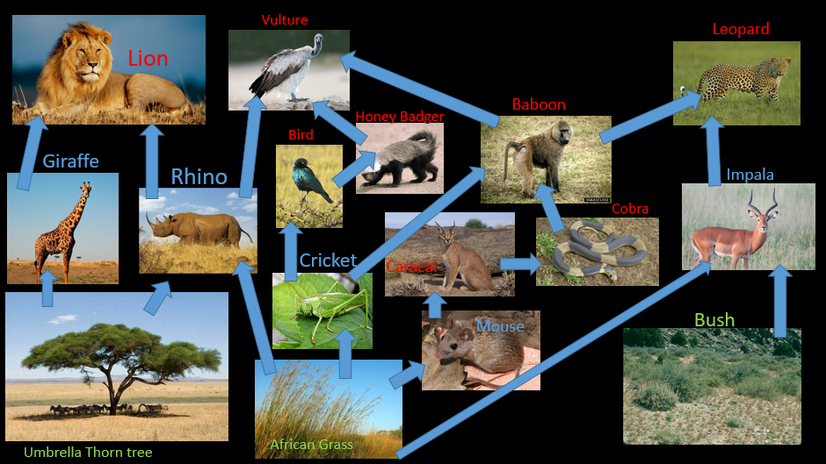
The African savanna ecosystem is a tropical grassland with warm temperatures year-round and with its highest seasonal rainfall in the summer. The savanna is characterized by grasses A food chain is a group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, prey to predators, and scavengers to This is an African Savanna Food Web.See if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. Look for: The Producers - the trees, shrubs and grass.. The Primary Consumers - the zebras and elephants.. The Secondary Consumers - the cheetah, hyena.. The Scavengers - the termites, vultures and hyena.. The Decomposers or Detritivores - mushrooms To understand the African Savannah Food Web, first read about the African Savannah Biome using this link.. Then read about the different trophic levels of a typical Food Chain (below). The trophic level is the position that an organism (plant or animal) occupies in a food chain - what it eats, and what eats it.