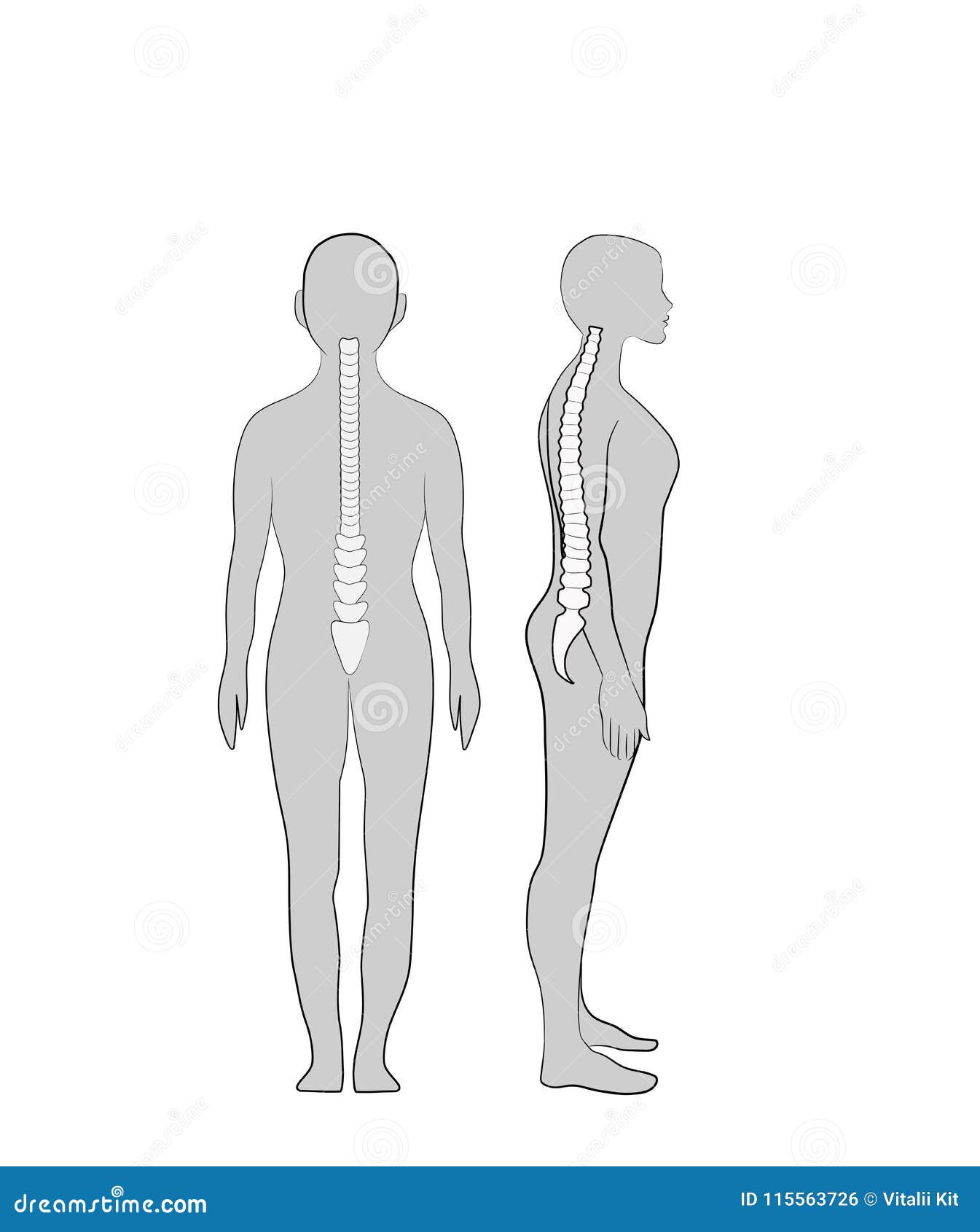
Body posture variations and landmarks for the alignment Biology Diagrams Chapter 4: Body Alignment, Posture, and Gait in 1926 by Professor Coighill of the Wistar Institute in London and by Dr. Mungo Douglass in 1937 in his text on anatomy. Sir Charles S. Sherrington, the Nobel Prize-winning physiologist, praised Alexander for his discovery, as did educator John Dewey and Dr. Frank P. Jones, Research Associate at Classically, ideal static postural alignment (viewed from the side) is defined as a straight line (line of gravity) that passes through the earlobe, the bodies of the cervical vertebrae, the tip of the shoulder, midway through the thorax, through the bodies of the lumbar vertebrae, slightly posterior to the hip joint, slightly anterior to the

Whether it's walking with a bad ankle or holding your face with toothache pain, any imbalance, injury, or malfunction of tissue can affect posture. Your StrongPosture® program will get each link working correctly, restoring normal motion… creating the foundation for great posture, and an active, pain-free lifestyle.
Assessment of Posture Biology Diagrams
Posture is a highly individual and dynamic aspect of human physiology. It is more about how your body adapts and interacts with different situations than a fixed 'correct' or 'incorrect' state. Posture can be simply defined as the way in which we hold our bodies while standing, sitting, or lying down.[1] Base of support. Any part of an object in contact with a surface that is, therefore, supporting it is described as its base of support. This can alter and depends on whether the object is static or in motion and, where the human body is concerned, will depend on the specific posture adapted at any particular time.
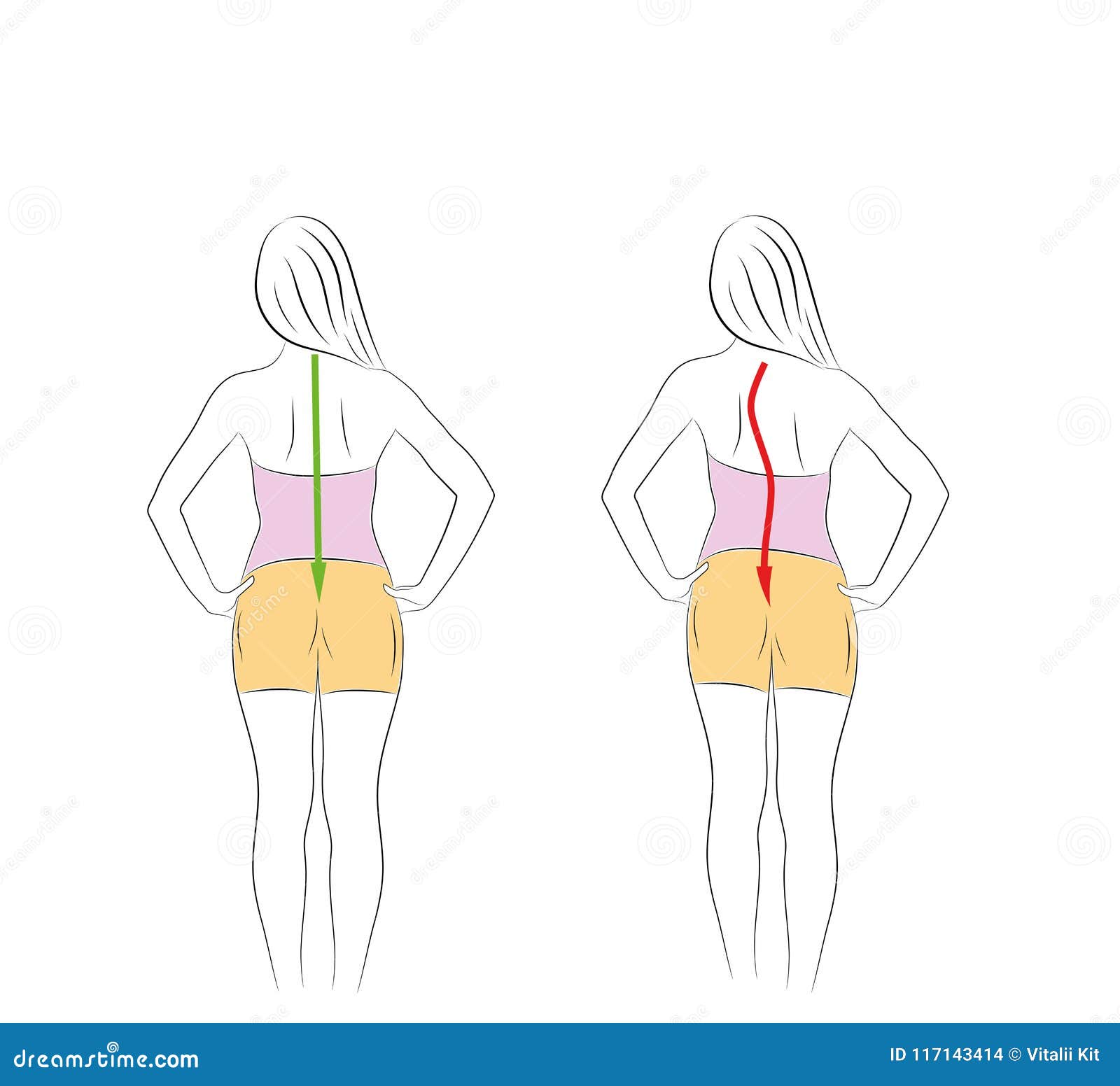
Poor posture and balance can lead to a range of physical problems, including back pain, neck pain, and falls. Common posture and balance problems include: Forward head posture: When the head is positioned forward, it places additional strain on the neck and upper back muscles. The Anatomy of Posture is the interconnected segments that assist each other. The Head, Spine, Rib Cage, Pelvis, Upper, and Lower Extremities. Balancing the muscles of the front and back of the torso will lead to ease of sitting and standing alignment. Spine. The spine can be considered the central column of the body with the major segments Background and aim of work: posture is the position of the body in the space, and is controlled by a set of anatomical structures. The maintenance and the control of posture are a set of interactions between muscle-skeletal, visual, vestibular, and

Good posture and how it can be achieved Biology Diagrams
By 1996 this proposed model was accepted in the scientific literature and published in the renowned medical journal, SPINE. In summary, the front view of the spine and posture should be straight. This alignment allows the body the best opportunity for equal and bilateral muscle effort and maintenance of posture with minimal energy expenditure.

