Chromosome instability in neuroblastoma A pathway to Biology Diagrams In turn, this could cause multipolar cell division and gross aberrations in chromosome number. Several well-known cancer risk factors could contribute to these processes. For instance, breakage-fusion-bridge instability can be induced directly by clastogenic substances, whereas papilloma virus infection has been shown to dysregulate centrosome
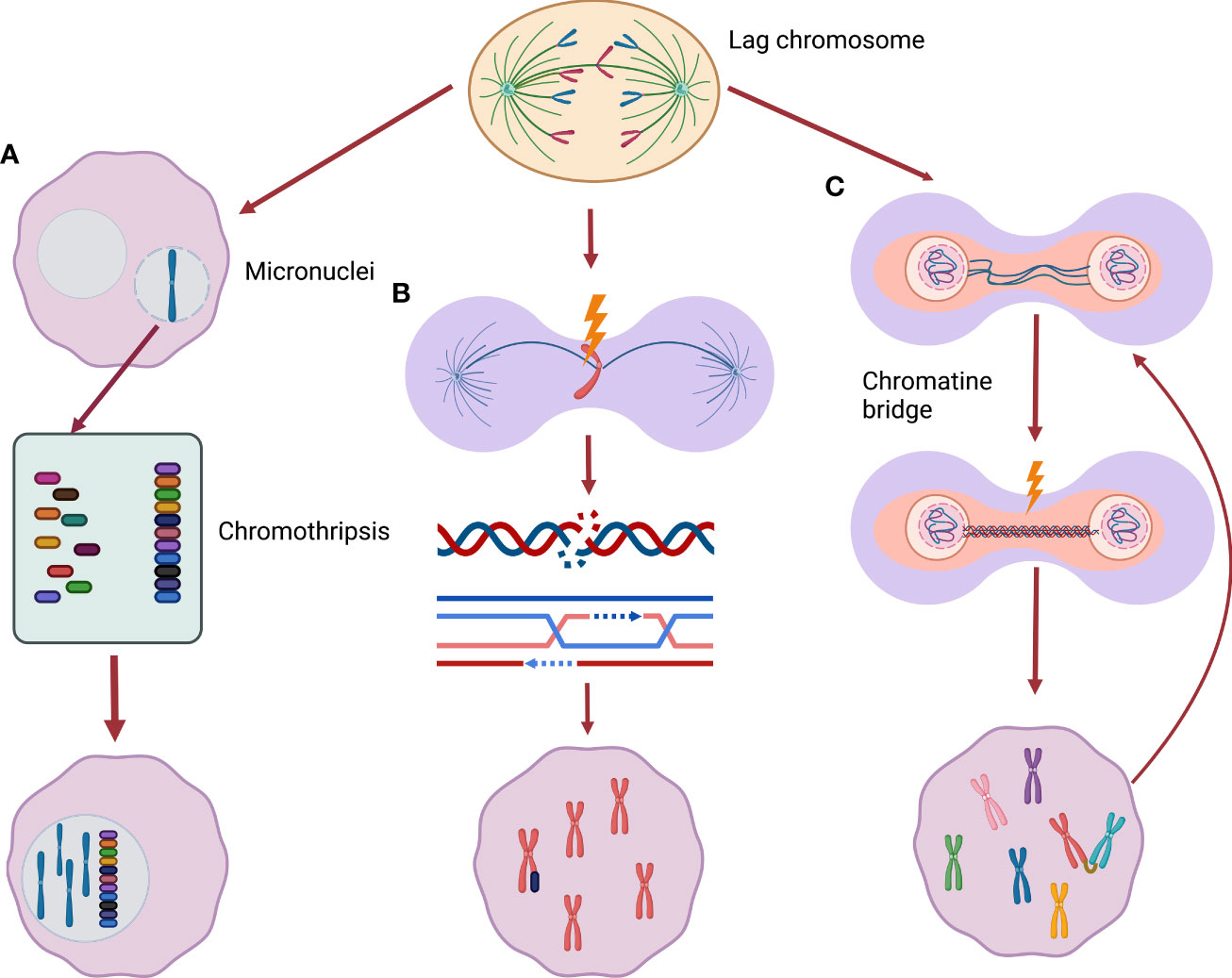
Chromosome instability describes an increased rate of chromosome missegregation in mitosis resulting in an incorrect chromosome number and/or abnormal chromosome structure cell carcinoma tumors and leukoplakia samples by promoter hypermethylation and its relation with microsatellite instability phenotype. Cancer. 2007;109:703-712. doi: 10

Targeting chromosomal instability in patients with cancer Biology Diagrams
For instance, four hallmarks of cancer have recently been included, which in addition to being involved in cancer development, could be involved in therapeutic responses and resistance. One of these hallmarks is chromosome instability (CIN), a source of genetic variation in either altered chromosome number or structure. Chromosomal instability (CIN) is a hallmark of human cancer and it is associated with poor prognosis, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance. CIN results from errors in chromosome segregation during mitosis leading to structural and numerical
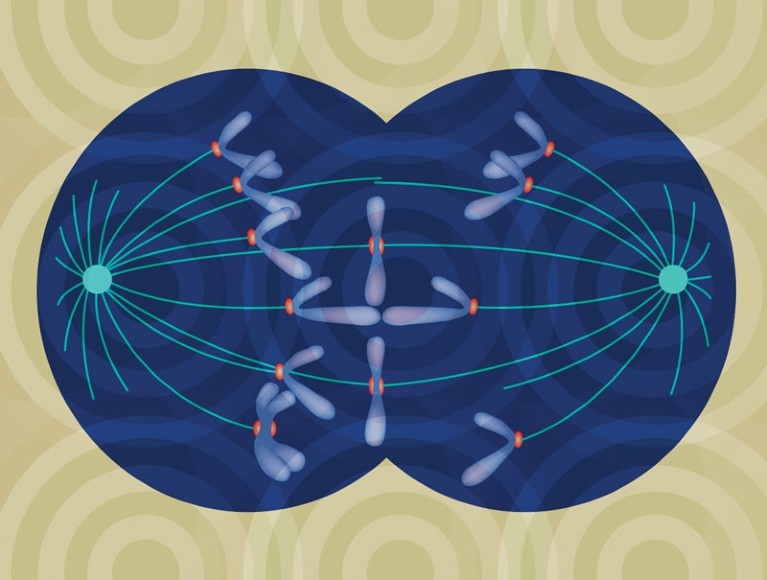
Chromosome Instability in Cancer 5 B. Measuring Chromosome Instability Traditionally, a high number of chromosome aberrations in a cell has been taken as evidence for chromosomal instability. Many in vitro studies trying to correlate genomic instability with specific gene changes have thus used aneuploidy as evidence of instability (Agapova et Chromosomal instability (CIN) is a hallmark of cancer and is associated with tumor cell malignancy. CIN triggers a chain reaction in cells leading to chromosomal abnormalities, including

What is chromosomal instability? Biology Diagrams
Chromosome instability (CIN) refers to an ongoing rate of chromosomal changes and is a driver of genetic, cell-to-cell heterogeneity. It is an aberrant phenotype that is intimately associated with cancer development and progression. The presence, extent, and level of CIN has tremendous implications … Chromosomal instability (CIN) arises from ongoing chromosome missegregation in cancer cells. a, During cytokinesis, the missegregated chromosome is randomly partitioned into the daughter cells In cancer, there are often large-scale deletions, rearrangements or other disruptions to our genetic information, which lead to a phenomenon known as chromosomal instability. This process has long been recognized, but new discoveries are helping us to better understand its role in cancer development.

