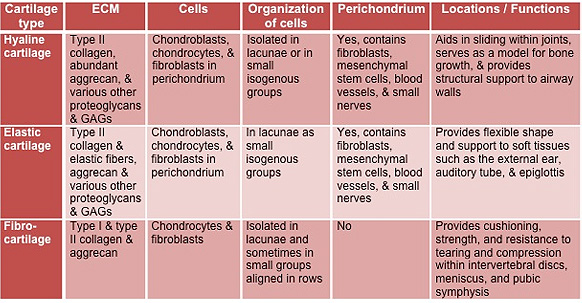
Classification And Structure Of Bones And Cartilages Biology Diagrams Key Terms. chondroitin sulfate: An important structural component of cartilage that provides much of its resistance to compression.. connective tissue: A type of tissue found in animals whose main function is to bind other tissue systems (such as muscle to skin) or organs.It consists of the following three elements: cells, fibers, and a ground substance (or extracellular matrix).
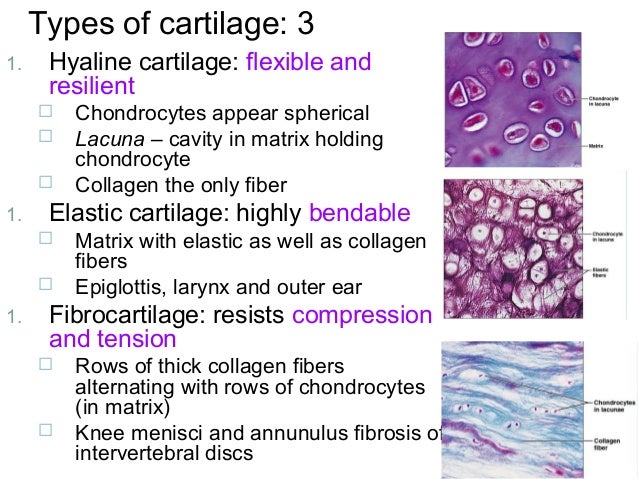
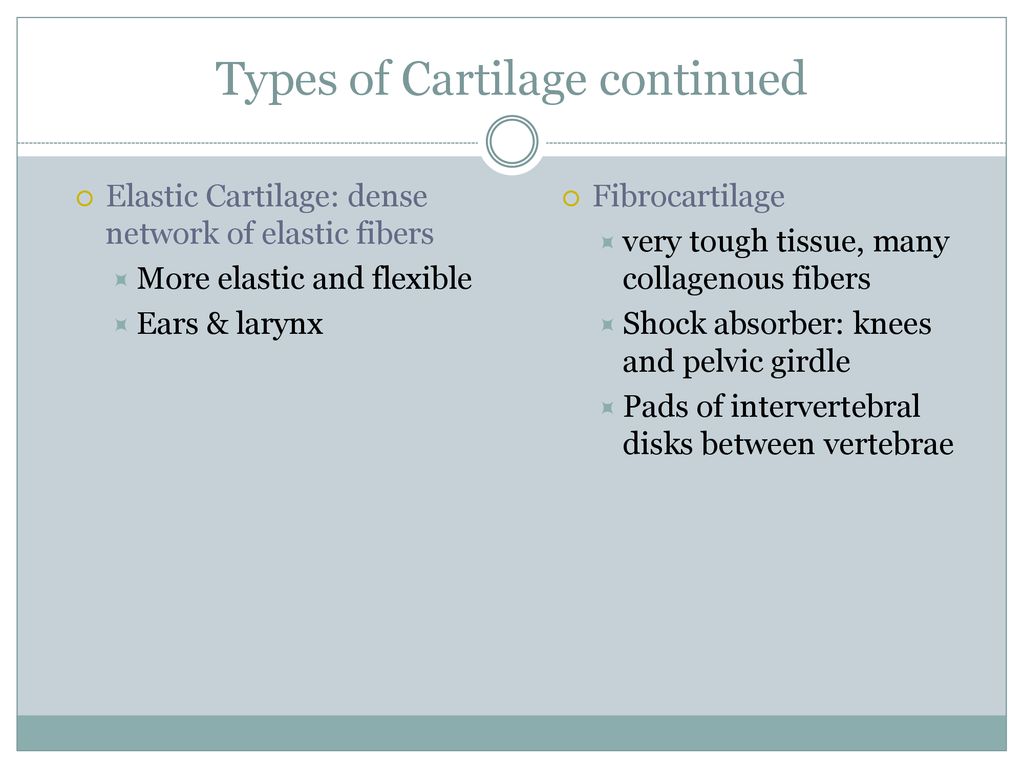
Cartilage serves as a barrier for your bones and joints. It protects the articular surfaces of your bones and provides padding for your joints. It is the function of cartilage to work: As a shock absorber for your bones and joints, cartilage helps make regular motions pain-free. making everyday activities more comfortable. Types of cartilage. Image Source: Physiopedia. Elastic cartilage is the most flexible type of cartilage that provides support to body parts requiring bending and movement for proper function. Elastic cartilage can return to its previous shape even after enduring high pressure. Elastic cartilage is found in structures like the larynx, eustachian tubes, and external ear that require both support

Skeletal Cartilages : Anatomy & Physiology Biology Diagrams
Hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage in your body. It lines your joints and caps the ends of your bones. It supports parts of your body that need to bend and move to function. Elastic cartilage can bounce back to its original shape, even after a strong force. Your ear is made of elastic cartilage. It can bend and move

Cartilage is the main type of connective tissue seen throughout the body. Different types of cartilage are found in joints, bones, spine, lungs, ears, and nose. What is the Function of a Cartilage? Cartilage serves various structural and functional purposes. It provides flexibility to bones and helps in smooth movements of bones and joints. Cartilage has many functions, including the ability to resist compressive forces, enhance bone resilience, and provide support in bony areas where flexibility is needed (see Image. Cartilage and Bone Illustration). The primary cell that makes cartilage is the chondrocyte, which resides within the lacunae. The cartilage matrix consists of fibrous tissue and various combinations of proteoglycans

Anatomy, Cartilage Biology Diagrams
Cartilage function is more than structural, and has different functions in the life cycle. In the embryo, it provides support and is a precursor to bone . Embryonic cartilage either remains as cartilage or provides a substructure for endochondral ossification, meaning it also functions as a template for the rapid growth and development of the
Cartilage is a connective tissue type (one of 6 major types) that is an essential part of many of the structures in the body. Cartilage is stiffer and less flexible than muscle, but not as rigid or hard as bone. Cartilage provides shape to some parts of the body, and acts as cushion between bones in joints. Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in multiple areas of the body, including joints, the ear and nose, and intervertebral discs. Hyaline cartilage, the most abundant type of cartilage, plays a supportive role and assists in movement.. Formed by the process of chondrogenesis, the resulting chondrocytes are capable of producing large amounts of collagenous extracellular matrix and Basic Structure, Types, and Locations. A skeletal cartilage is made up of some variety of cartilage tissue molded to fit its body location and function. Cartilage consists primarily of water, which accounts for its resilience, that is, its ability to spring back to its original shape after being compressed.