cortical functional areas lateral view Diagram Biology Diagrams The cerebral cortex lobes include the parietal, frontal, occipital and temporal lobes. It is divided into four lobes that each have a specific function. For example, there are specific areas involved in movement and sensory processes (vision, hearing, somatosensory perception (touch), and olfaction). Other areas are critical for thinking These functions are processed by an area of your parietal lobe called the somatosensory cortex. Processing hearing information. This function is processed by an area of your temporal lobe called the auditory cortex. Processing taste and flavor. These functions are processed by an area of your frontal lobe called the gustatory cortex. Another fascinating avenue of research involves the Pallium Brain: Exploring the Complex Structure and Functions of the Cerebral Cortex. This outer layer of the brain, which includes all the lobes we've discussed, is a key area of interest for researchers trying to understand higher cognitive functions. Understanding the structure and

The cerebral cortex is composed of a complex association of tightly packed neurons covering the outermost portion of the brain. It is the gray matter of the brain. Lying right under the meninges, the cerebral cortex divides into four lobes: frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes, each with a multitude of functions. It is characteristically known for its bulges of brain tissue known as It includes all of the lobes of the cortex except the limbic lobe and consists of six layers of cells or laminae. total of 52 areas which have been shown to have distinct neuronal organization and have also been correlated to various cortical functions. Important Brodmann areas; Frontal lobe: Primary motor cortex (Area 4), premotor cortex
Lobes of the brain Biology Diagrams
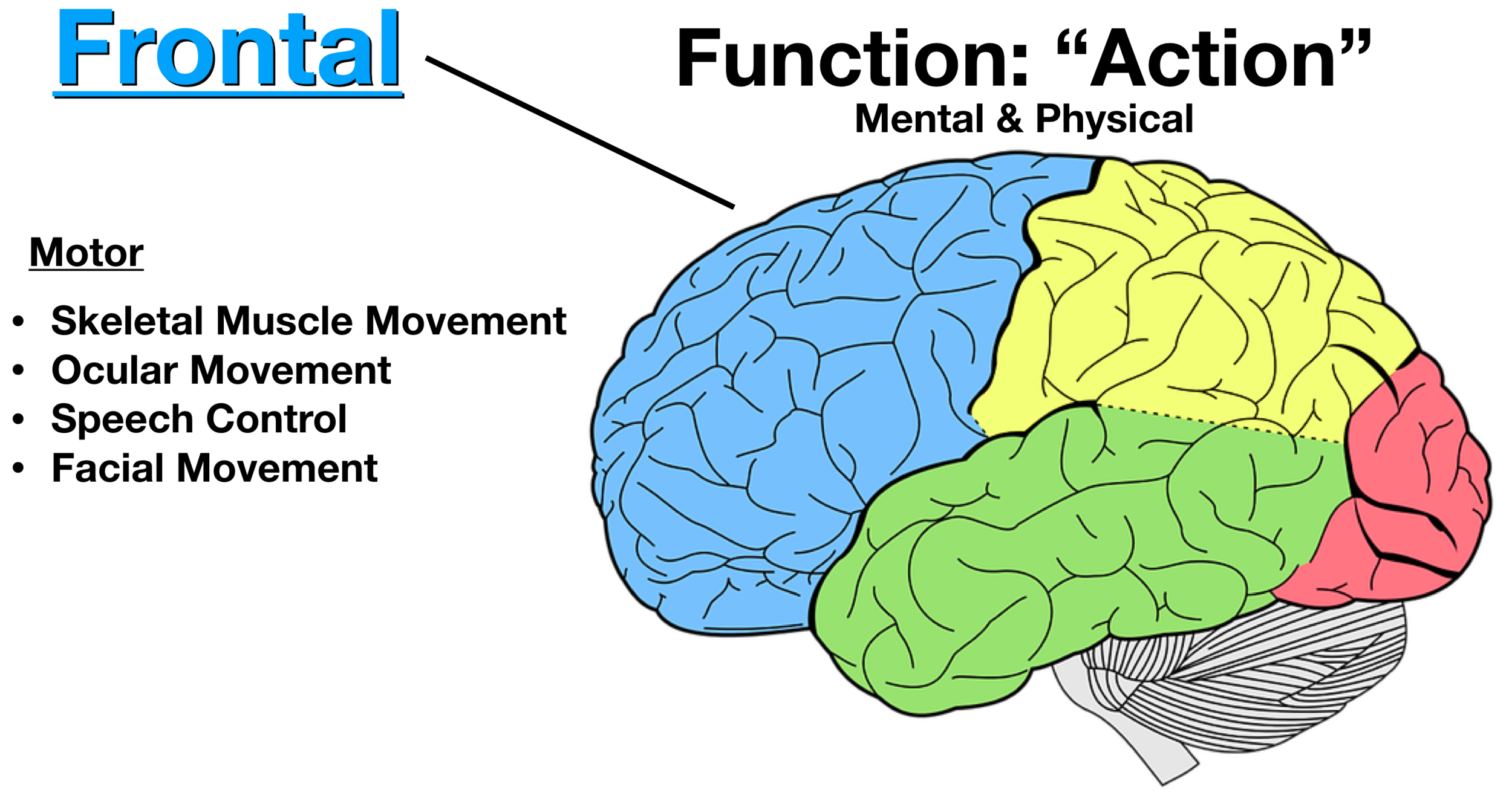
The motor cortex corresponds to the precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe. The precentral gyrus contains the primary motor cortex (Brodmann area 4), which is responsible for integrating signals from different brain regions to modulate motor function. The primary motor cortex is where the corticospinal tract originates. Anterior to the primary motor cortex of the precentral gyrus is the premotor
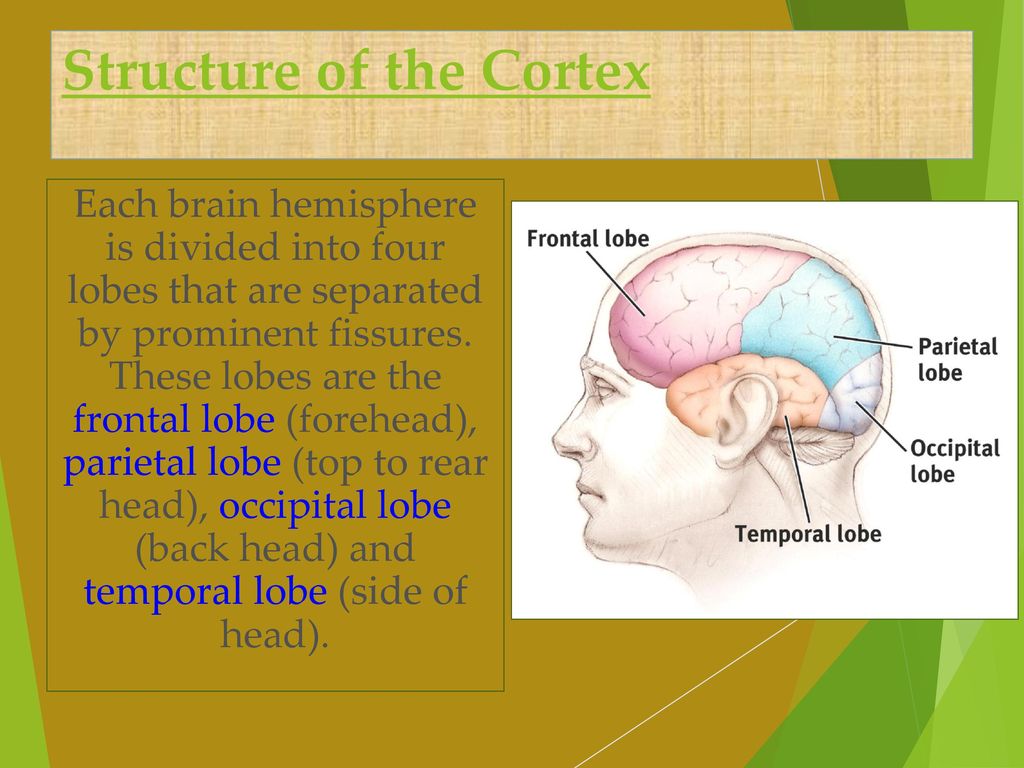
Explore the four lobes of the brain's cerebral cortex: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital. Learn their functions and interactions in cognition. Imagine being able to boost memory function by targeting the temporal lobe, or enhance visual processing by stimulating the occipital lobe. While such possibilities raise ethical questions These lobes are called the frontal lobes, temporal lobes, parietal lobes, and occipital lobes. Lobes and their Functions. The cerebral cortex, which is the outer surface of the brain, is associated with higher level processes such as consciousness, thought, emotion, reasoning, language, and memory. The insular cortex is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus (the fissure separating the temporal lobe from the parietal and frontal lobes). The insular cortex has an important function for sending axons to the amygdala and responding to tones and somatosensory stimulation. [12]

