Discovering nonrandom segregation of sister chromatids Biology Diagrams Separation Of Sister Chromatids. The separation of sister chromatids is a crucial step in cell division. This process ensures that each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes. Understanding the stages involved can provide insight into how cells maintain genetic consistency. Anaphase. During anaphase, the sister chromatids are
Separation of Sister Chromatids during Anaphase. During the congression of chromosomes at the metaphase plate, when some kinetochores are unattached to the spindle, an active signal inhibits the onset of anaphase. This involves the Mitotic Checkpoint Complex or the MCC. The MCC contains proteins that primarily inhibit the activity of the
Anaphase II and How Sister Chromatids Separate Biology Diagrams
The separation of sister chromatids during anaphase requires the cleavage of remaining cohesion by Separase. The second wave of cohesin removal is scheduled to anaphase. During anaphase, sister chromatids are separated and then segregated to the opposite poles of the spindle. The separation and poleward movement of sister chromatids is
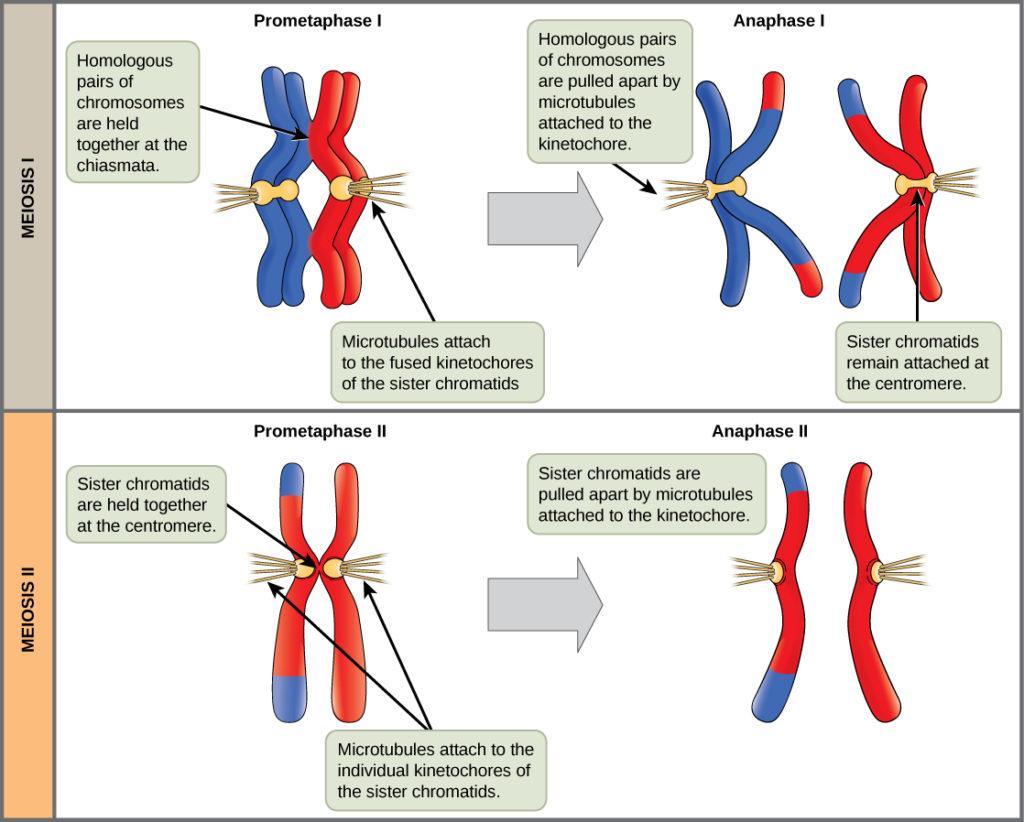
Sister chromatids in meiosis. Meiosis is similar to that mitosis and is a two-part cell division process. In Prophase I and Metaphase I: movement of the sister chromatids in both the phages. In Anaphase: homologous chromosomes move to the opposite pole, and sister chromatids remain attached. The separation of the sister chromatids does not occur until anaphase II.

Sister Chromatids - Definition, Functions and Structure Biology Diagrams
Anaphase II resembles mitosis, focusing on sister chromatid separation. Anaphase I establishes the haploid state, while Anaphase II ensures proper chromosome distribution within that framework. Centromere behavior also differs. In Anaphase I, cohesin proteins keep sister chromatids together, protected by Shugoshin. This connection is pivotal for the movement and eventual separation of chromatids. During anaphase, the spindle fibers shorten, pulling sister chromatids apart toward opposite poles of the cell. This separation is regulated by the anaphase-promoting complex, which triggers the degradation of cohesin proteins holding the chromatids together.
Sister chromatids, identical copies of a chromosome, are separated during cell division to ensure the accurate distribution of genetic material to daughter cells. This separation occurs during the metaphase and anaphase stages of mitosis, as well as during the first meiotic division, meiosis I. Sister chromatids are held together by a protein complex called cohesin until the appropriate stage

Sister Chromatid Separation In Cell Division Biology Diagrams
The paternal (blue) chromosome and the maternal (pink) chromosome are homologous chromosomes.Following chromosomal DNA replication, the blue chromosome is composed of two identical sister chromatids and the pink chromosome is composed of two identical sister chromatids.In mitosis, the sister chromatids separate into the daughter cells, but are now referred to as chromosomes (rather than

