Finalistas Pires Quesado 2009 coral reef food chain pictures Biology Diagrams The food webs are a very important factor in the safeguard of the coral reef ecosystemFood webs protect the fragile balance there is between species; there are just the right amount of predators and prey within the aforementioned trophic levels. We start to see the importance of the balance set by the food webs when we see the consequences of anthropological interferences in those food webs. Learn about the trophic levels, energy transfer, and predator-prey relationships in a coral reef ecosystem. Explore the illustration and answer questions about the organisms and their roles in the food web.
This is a Coral Reef Food Web.See if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. Look for: The Producers - the phytoplankton on the ocean's surface.. The Primary Consumers - the coral, sea turtle, and fish.. The Secondary Consumers - the sharks, anemones, starfish, baracuda, jellyfish, sea snakes and sea slugs.

Conceptual food web of a coral reef ecosystem identifying 16 key ... Biology Diagrams
Learn how the marine animals of the reef are interconnected in a complex food chain with multiple levels. See a diagram of the food web and how human influence threatens its balance.

Learn how matter and energy are recycled and transferred in a coral reef ecosystem. Explore the biogeochemical cycles, feeding strategies, and food web of the coral reef.
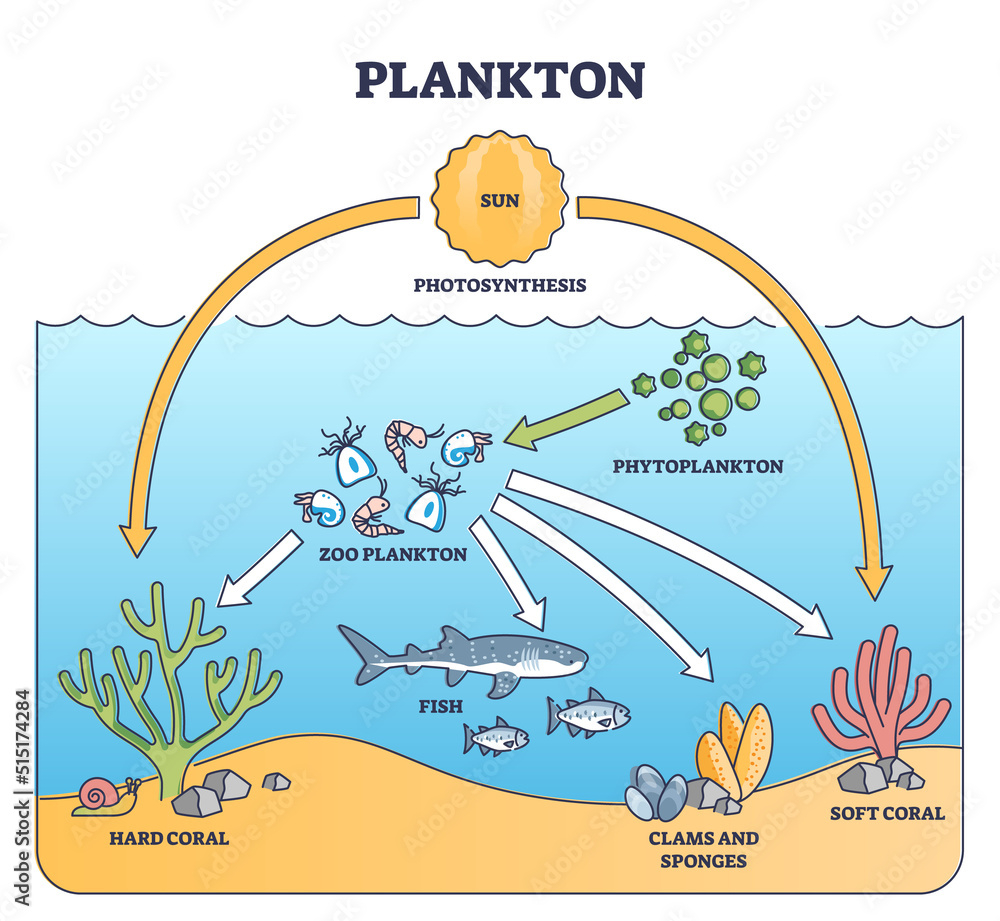
Science Learning Hub Biology Diagrams
A food web consists of all the food chains in a single ecosystem.Each living thing in an ecosystem is part of multiple food chains. Each food chain is one possible path that energy and nutrients may take as they move through the ecosystem. Not all energy is transferred from one trophic level to another. Energy is used by organisms at each trophic level, meaning that only part of the energy This process is very important and means that even top-level consumers are contributing to the food web as the decomposers break down their waste or dead tissue. Changes to food webs. The effect of removing or reducing a species in a food web varies considerably depending on the particular species and the particular food web.
