Forest Food Chain Biology Diagrams The hairy woodpecker is a medium-sized woodpecker found across much of North America. Like other woodpeckers, it plays an important role in the ecosystem by creating cavities in trees for nesting and roosting sites. The hairy woodpecker's diet consists mainly of insects, especially the larvae of wood-boring beetles. Woodpeckers are essential to the animal food chain as prey and predators. In their role as prey, they provide food to many organisms, thus promoting survival. As predators, woodpeckers help regulate the local population of the different kinds of insects they feed on. In essence, they promote the existence of a balance in their ecosystem.

Woodpecker Diet and Food Sources. Woodpeckers as wild birds can easily find abundant food sources in the wild. However, the exact foods for woodpeckers vary, depending on their species. The most common foods include suet, insects, peanuts, peanut butter, black oil sunflower seeds, nectar, sap, acorn, etc. 1. Insects
What do Woodpeckers Eat and how do they find their food? Biology Diagrams
The woodpecker family, Picidae, fills a unique niche in the food-gathering chain. Woodpeckers drill into trees to uncover insect food, to create nesting shelters and to communicate with other woodpeckers. A number of body adaptations make this drilling possible. A woodpecker has a sharp, stout bill with a chisel-like tip for

The adaptation of specialized teeth for crunching through exoskeletons underscores their evolutionary niche in the food chain. C. Fruits and Vegetation. Inclusion of Fruits, Vegetables, and Plant Matter Ecologically, woodpeckers' diets resonate in forest ecosystems, exerting influence on insect populations and tree health. Opossums, with

"Feeding Habits Unveiled: A Deep Dive into the Diets of Woodpeckers and ... Biology Diagrams
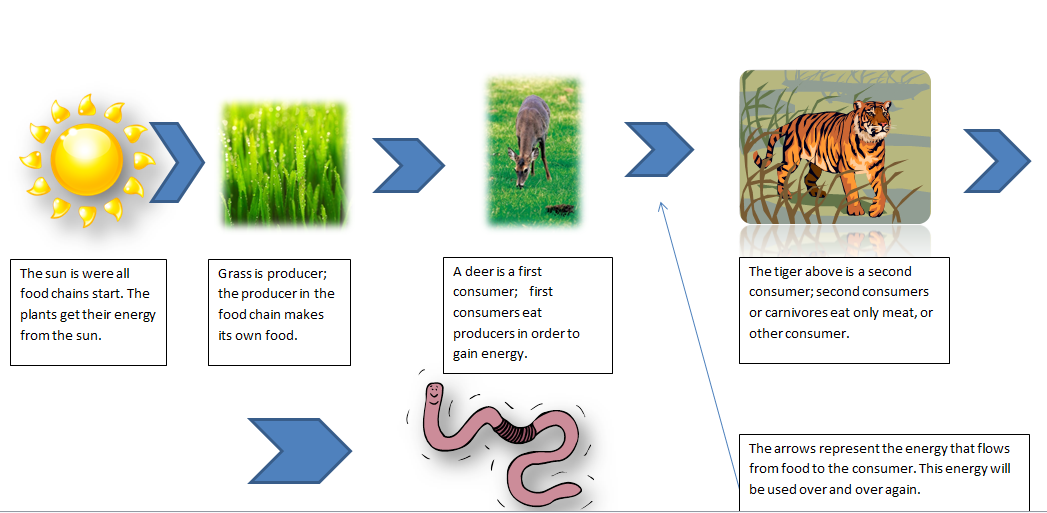
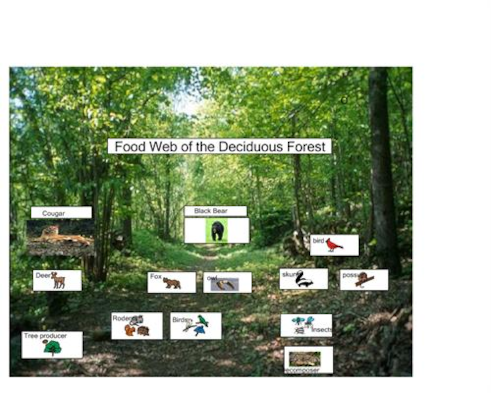
Acorns are a preferred food for various birds, including woodpeckers, jays, and pigeons, as well as mammals such as squirrels, deer, and wild boars. The primary food chain in a forest ecosystem consists of producers such as plants that use photosynthesis to create their own food, primary consumers such as herbivores that eat the producers