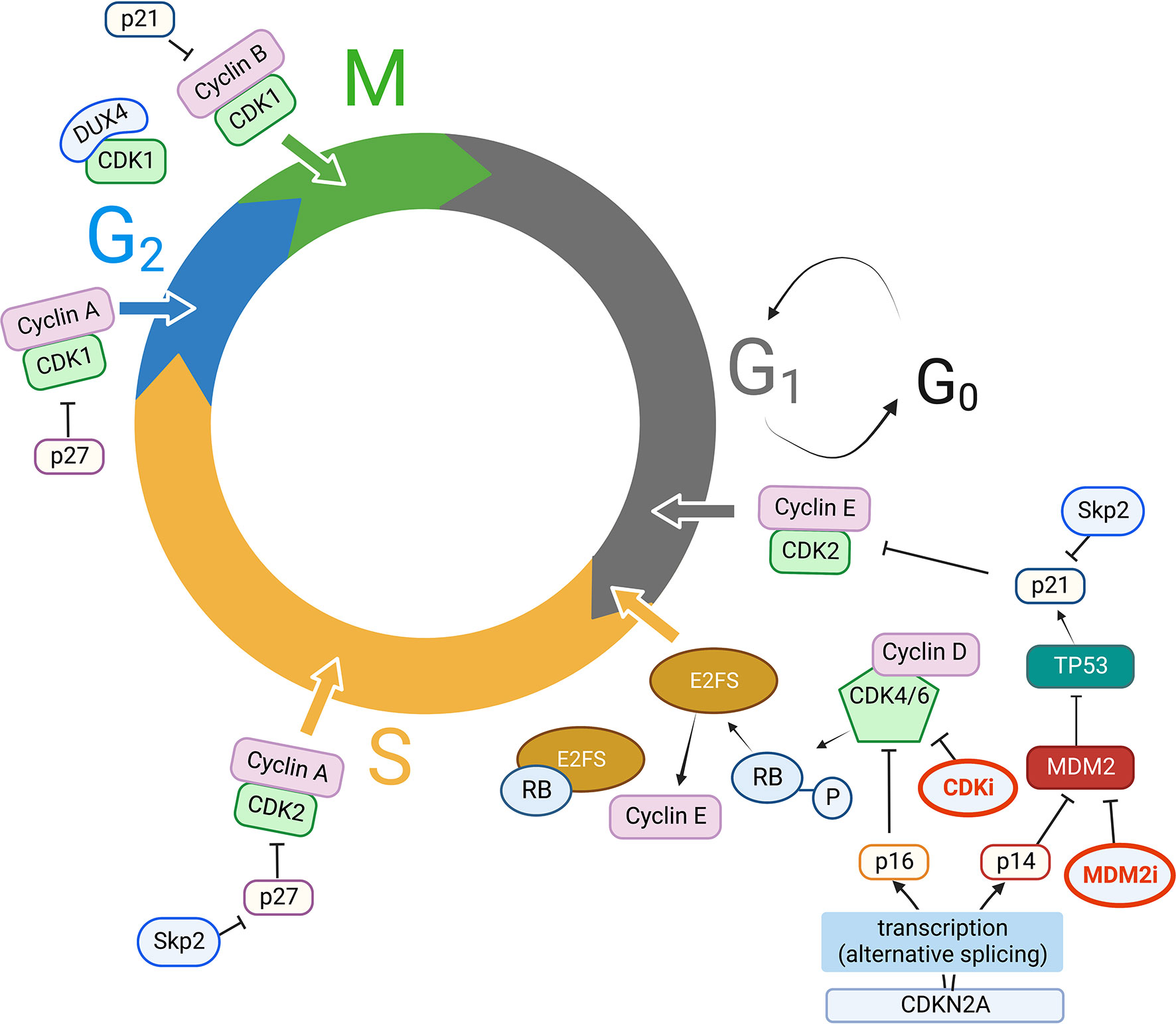
How the Cyclin Became a Cyclin Cell Biology Diagrams To determine if the CRL2 ZYG-11 pathway for cyclin B1 degradation is conserved in humans, we tested for the interaction of human ZYG11B with cyclin B1. We observed that FLAG-tagged ZYG11B coimmunoprecipitated with endogenous cyclin B1 in HEK293T cells, indicating physical interaction (Fig. 2 A). Cyclin Dependent Kinases (CDKs) are closely connected to the regulation of cell cycle progression, having been first identified as the kinases able to drive cell division. In reality, the human

Ras activity regulates cyclin E degradation by the Fbw7 pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:9649-54. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Welcker M, Orian A, Jin J, Grim JE

Cyclin D degradation by E3 ligases in cancer progression and treatment Biology Diagrams
Cyclin degradation is the key step governing exit from mitosis and progress into the next cell cycle. When a region in the N terminus of cyclin is fused to a foreign protein, it produces a hybrid protein susceptible to proteolysis at mitosis. During the course of degradation, both cyclin and the hybrid form conjugates with ubiquitin. Cyclin degradation during the cell cycle. The progression of eukaryotic cells through the division cycle is controlled in part by the synthesis and degradation of cyclin B, which is a regulatory subunit of the Cdc2 protein kinase. The proteins susceptible to degradation by this pathway are thought to be normally long-lived but dispensable Check out the QIAGEN pathway database for relevant molecules interactions. caused by the degradation of Cyclin B, is required for exit from mitosis. 14-3-3 proteins bind to phosphorylated CDC2-Cyclin B kinase and export it from the nucleus. During G2 phase, CDC2 is maintained in an inactive state by the kinases Wee1 and Myt1. As cells

This pathway is regulated by growth factor receptors that provide a direct link from growth factor signaling to the regulation of cyclin D1 stability and accumulation Loss of Fbxo4 results in reduced cyclin D1 degradation and triggers a corresponding increase in CDK4/6 activity and a tumor prone phenotype in Fbxo4 deficient mice [117, 118]; OA inhibits cyclin B proteolysis if added before entry into mitosis. H1 kinase activity, the phosphorylation-induced mobility shift of 35 S-labeled Cdc25 and of Cdc27, and the degradation of 35 S-labeled cyclin B (Cyc B) were analyzed in extracts treated either with buffer (A) or with 1 μM OA (B and C), which was added either at time zero (B) or 25 min later (C).