Human body systems Body systems Paranasal sinuses Biology Diagrams Nostrils (nares): Your nostrils are holes that lead to your nasal cavities. Paranasal sinuses: These air-filled pockets connect to your nasal cavities. They produce the mucus that keeps your nose moist. Septum: This is the bone and cartilage that separate your nasal cavities. The lower part of your septum sits between your nostrils. The nasal septum (Latin: septum nasi) separates the left and right airways of the nasal cavity, dividing the two nostrils. Anatomy figure: 33:02-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Diagram of the skeleton of the medial (septal) nasal wall"

A. Nasal Septum. The nasal septum is a thin wall inside the nose that separates the nasal cavity into left and right sides, creating two nostrils. At the front, the visible part called the columella nasi, is made of soft tissue and cartilage. The septum itself is about 2 mm thick and is built from a mix of bone and cartilage. Here we will discuss the anatomy of the nasal skeleton and its component bones. Premium Feature 3D Model. Pro Feature. The internal nasal septum separates the nasal cavity into two nostrils. The bones that contribute to the nasal septum can be divided into: It is one of the most complex bones in the human body,
The Nasal Skeleton Biology Diagrams
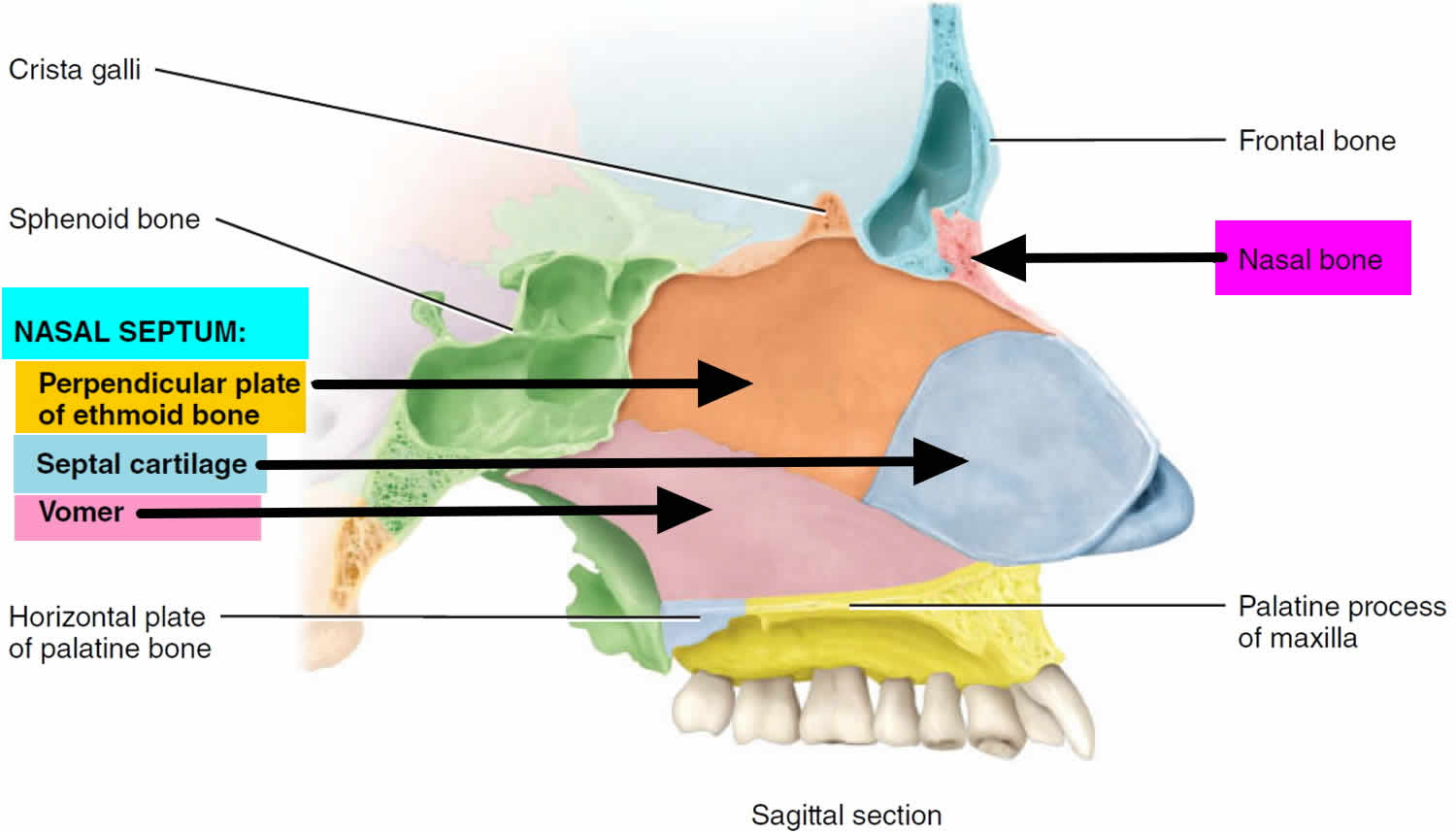
The nasal septum separates the left and right airways in the nose, dividing the two nostrils.It is depressed by the depressor septi nasi muscle.The fleshy external end of the nasal septum is sometimes also called columella. The nasal septum contains bone and hyaline cartilage.The nasal septum is composed of five structures: perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone vomer bone cartilage of the septum

Anatomy atlas of the nasal cavity: fully labeled illustrations and diagrams of the nose and paranasal sinuses (external nose, nasal cartilages, nasal septum, nasal concha and meatus, bones of the nasal cavity and vessels and nerves). The nasal septum is the midline vertical partition which separates the nasal cavity into left and right halves, Marieb, E., & Hoehn, K. (2022). Human Anatomy and Physiology, Global Edition. (12th ed.). Pearson Education, Limited. Sinnatamby, Chummy S. Last's Anatomy E-Book : Last's Anatomy E-Book, Elsevier Health Sciences, 2011.
The Anatomy of the Nose: Understanding Its Structure and Function Biology Diagrams
The nasal septum is a thin, vertical structure that divides the nasal cavity into two symmetrical halves—left and right. It is made up of both bone and cartilage, providing support and shape to the nose.[8] Atlas of Human Anatomy. 7th ed. Elsevier; 2018. ISBN 978-0323393225. McMinn RMH, Hutchings RT, Logan BM.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/nasal-septum-3/x6RqO4wPyKqh6xFusJp8w_Nasal_Septum.png)
Sometimes, the septum takes the shape of a V, blocking one nostril completely. In other instances, it assumes an S shape, obstructing both nostrils. A deviated septum can lead to breathing difficulties, snoring, sleep apnea, and increased susceptibility to sinus infections. To assess the septum and its position, doctors use a nasal speculum. The nasal septum is in the midline of the nose and made of flat cartilage anteriorly and bone posteriorly. The anterior portion is made of irregular quadrangular hyaline cartilage that inserts into the nasomaxillary crest of the maxilla and nasal spine. Oneal RM, Beil Jr RJ, Schlesinger J. Surgical anatomy of the nose. Otolaryngol Clin

