Human Skeleton Ligaments Muscles Tendons Anatomy Stock Illustration Biology Diagrams Tendons and ligaments play an important role here, too: Tendons connect muscles to bones, allowing us to move, and ligaments help to hold things in place. Our bones, muscles and joints work together in a coordinated way to move our body and give it stability. Tendons and ligaments play an important role here, too: Tendons connect muscles to

Ligaments are bands of tissue that help hold bones, joints and organs in place. You can take several steps to protect your ligaments. However, ligament sprains are very common, especially in the ankle, knee, wrist, back and neck. Proper diagnosis and treatment can help you avoid worsening problems and live a fuller life.

Tendon: Function, Anatomy & Common Injuries Biology Diagrams
What is the anatomy of a tendon? Tendons are mostly collagen, one of the most abundant proteins in your body. Tendons also contain blood vessels and nerves. Advertisement. Collagen fibers are flexible, strong and resistant to damage. A tendon's structure is similar to a fiberoptic cable or a rope, with small collagen fibers arranged in bundles.

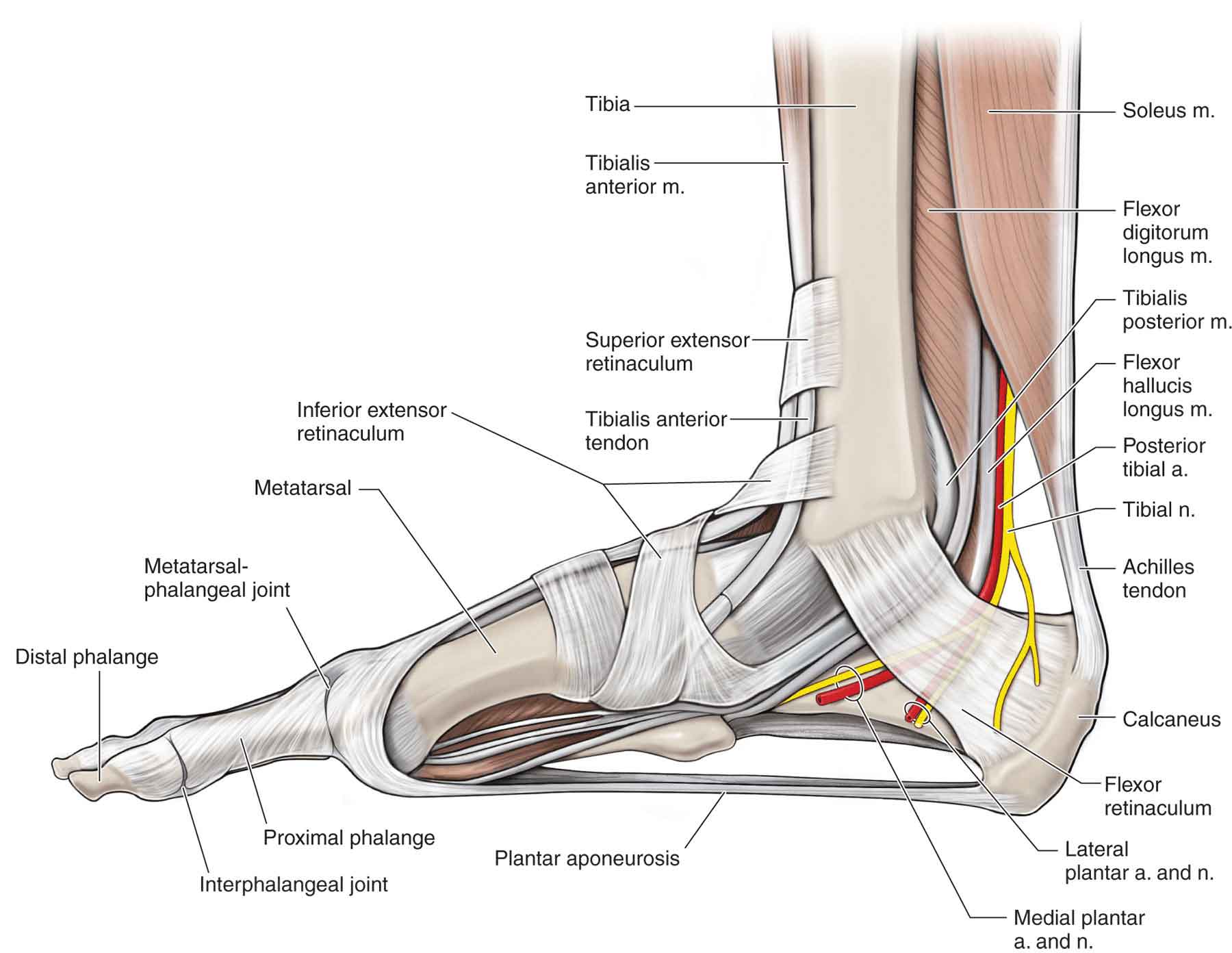
Tendon and ligament anatomy There are specialized areas of tendon and ligament at their at-tachments. The attachment of tendons and ligaments to bone is termed the enthesis, whilst the attachment of tendon to muscle is termed the myotendinous junction. There are two types of enthesis; fibrous and fibrocartilagi-nous. In a fibrous enthesis Tendons and ligaments are types of connective tissue made of collagen fibers. Tendons attach muscles to bones while ligaments attach bones to bones. Tendons and ligaments can become injured from trauma or overuse over time. Rest is needed following injuries to promote healing, while muscle strengthening is needed to return to unrestricted activity. A diagram illustrating knee anatomy could highlight both the ACL (ligament) and patellar tendon. Images showing muscle groups alongside their respective tendons could reinforce connections visually. Using color-coded diagrams may also help distinguish between these two structures easily—perhaps using blue for ligaments and red for tendons.

Tendon and Ligament Anatomy, Biology, and Biomechanics Biology Diagrams
The two cruciate ligaments are in the center of your knee. They keep your knee from shifting too far forward or backward. The ligaments of the knee are: Medial collateral ligament (MCL). Your MCL connects your thigh bone (femur) to your shin bone (tibia). Wide and flat, it gives stability to your inner knee. Lateral collateral ligament (LCL). Tendons and ligaments act as the bonds that tie the body together. Ligaments connect one bone to another at a joint, and tendons connect bone to muscle. While the specific natures of their tasks differ, tendons and ligaments share a great many features in their construction and function. Key Differences Between Ligaments and Tendons. Now that we've laid down some definitions, let's compare ligaments and tendons based on several criteria: 1. Function: - Ligaments connect bones to bones and provide stability to joints. As I found out mid-game, without healthy ligaments, movements can lead to joint instability and injury.