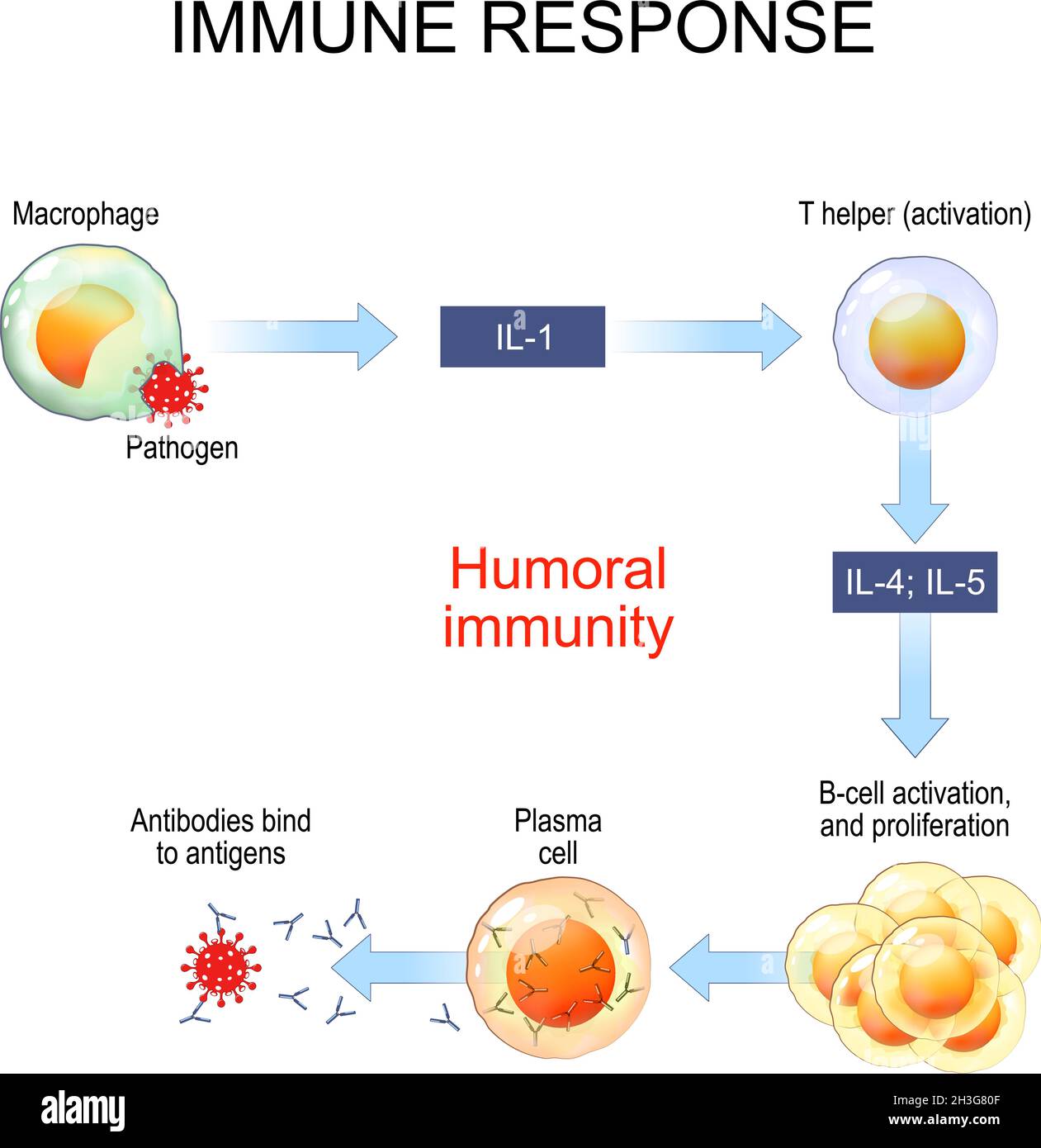
IMMUNOLOGY Mustansiriyah University College of Science Biology Diagrams Antibody production is the body's natural reaction to block viral infection in host cells or through the production of viral antigens on host cells, in which effector cells are responsible for eliminating infected target cells by interacting with antibodies. Yifan Ma, in Seminars in Immunology, 2009. Abstract. Antibody production is Understanding the engineering of these control systems represents a challenging future step for treating disorders of antibody production in autoimmunity, allergy and immunodeficiency

Home » Immunology. Antibody: Definition, Structure, Types, Forms, Functions. July 16, 2024 August 3, 2023 by Faith Mokobi. Some point mutations will result in the production of antibodies that have a weaker interaction (low affinity) with their antigen than the original antibody, and some mutations will generate antibodies with a stronger

An introduction to immunology and immunopathology Biology Diagrams
This article, titled "Antibody Production Notes," delves into a comprehensive exploration of antibody production, highlighting its profound significance and providing illuminating insights into the underlying mechanisms. Antibody production, a critical process in the field of immunology, plays a key role in producing an effective immune response against invading pathogens. Understanding the

Monoclonal Antibodies are the antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies can have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope. A technique to produce monoclonal antibodies was devised by Georges Kohler and Cesar Milstein in 1975. The method relies on fusing B cells from an immunized animal (typically a The representation of immune checkpoint molecules such as CTLA-4, production of regulatory cytokines like TGF-β and IL-10, and regulation of metabolic pathways via molecules such as CD73 and CD39 are the various techniques in which suppression occurs [30,31,32,33]. Furthermore, during inflammation and injury, Tregs preserve tissue homeostasis The antibody-production pathway begins when the B cell's antigen-binding receptor recognizes and binds to antigen in its native form. Local Th cells secrete cytokines that help the B cell multiply and direct the type of antibody that will be subsequently produced. Asthma & Clinical Immunology Volume 14 Supplement 2, 2018: Practical guide
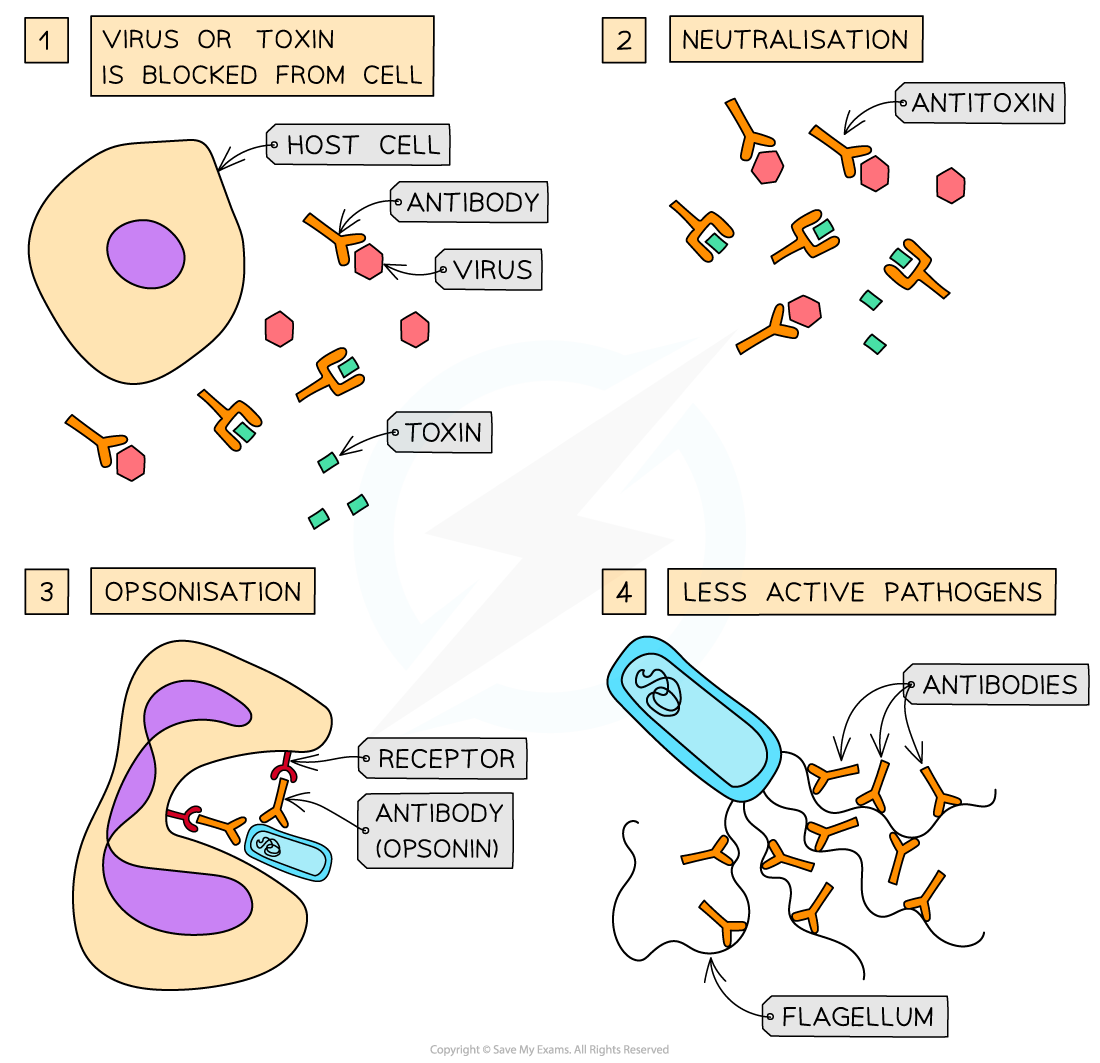
[PDF] Antibody Production Notes: 7 Comprehensive Steps Biology Diagrams
To eliminate the invader, the immune system calls on a number of mechanisms, including one of the most important—antibody production. Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called B lymphocytes (or B cells). When an antigen binds to the B-cell surface, it stimulates the B cell to divide and mature into a group of identical