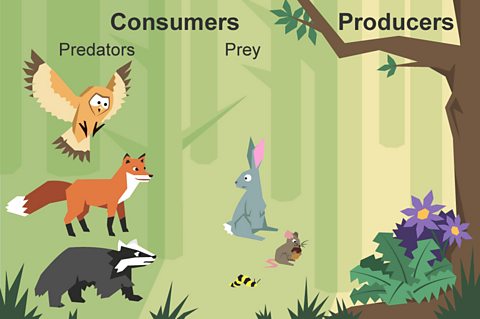
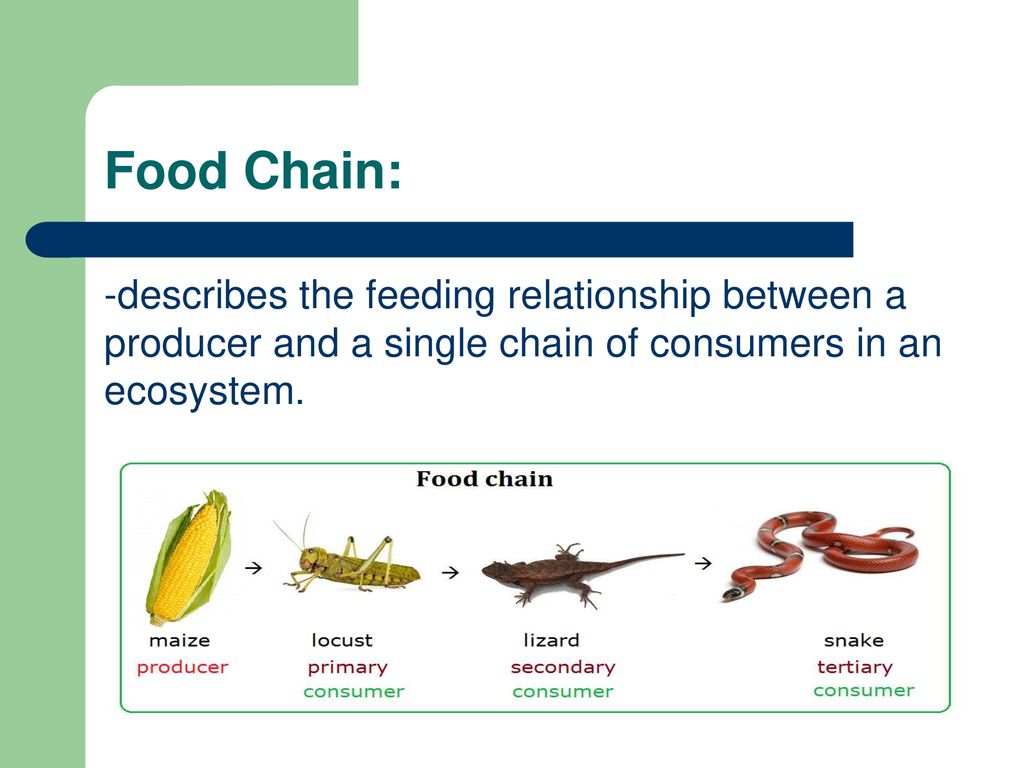
Living Things Need Energy Biology Diagrams Food Chains. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher-level consumers, and finally decomposers. These levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. There is a single path through a Organisms in the food chain are divided into trophic levels or feeding levels. The four essential parts are the sun, primary producers, consumers, and decomposers. Every food chain originates with the sun providing light and energy for plants to grow and ends with the decomposition of the animals.
+first+consumers+on+the+food+chain.jpg)
These organisms directly feed on plants or other producers. They play a very crucial role in transferring energy from plants to higher levels of the food chain. Secondary Consumers: Secondary consumers are organisms in a food chain that feed on primary consumers or other herbivores. They occupy the next level of the food chain and play a
Definition, Examples, Types Biology Diagrams
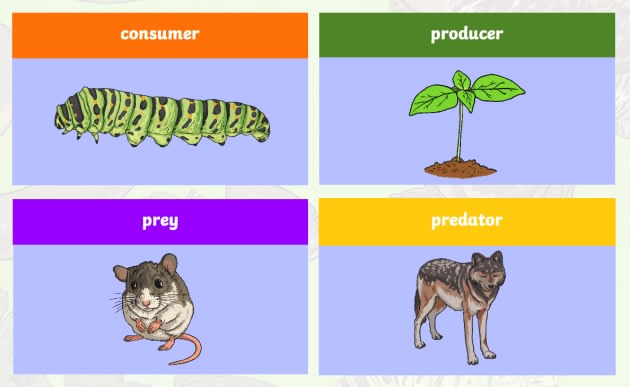
Examples of producers and consumers in science are all around the world. Explore the different plant and animal examples of producers and consumers. Trophic Levels Organisms in food chains are grouped into categories called trophic levels. Roughly speaking, these levels are divided into producers (first trophic level), consumers (second, third, and fourth trophic levels), and decomposers. Producers, also known as autotrophs, make their own food. They make up the first level of every food chain.
A food chain describes how living organisms get their food. All organisms, from the most complex to the most simple ones, need food to survive. Living things can be part of multiple food chains and all connected food chains in an ecosystem combine to make a food web.. As shown in the infographic below, a basic food chain is composed of producers, consumers, and decomposers. By studying food chains, ecologists better understand ecosystem dynamics, including the flow of energy, population control, and the impact of human activities on natural habitats. Key Points. Food chains are linear models that illustrate energy transfer from producers to top consumers. Each organism in a food chain contributes to ecosystem balance.
Food chain Definition and Examples Biology Diagrams
What Is A Food Chain? The food chain is a series of creatures that begins with producer organisms, having consumers at various levels in between, and ends with decomposer species. A food web connects numerous food chains. The food chain takes a single path, whereas the food web takes several paths. The food chain teaches us about the relationships between creatures.
A producer is an organism that makes its own food. Most food chains start with a green plant, because plants make their own food by photosynthesis. A consumer is a living thing that eats other

