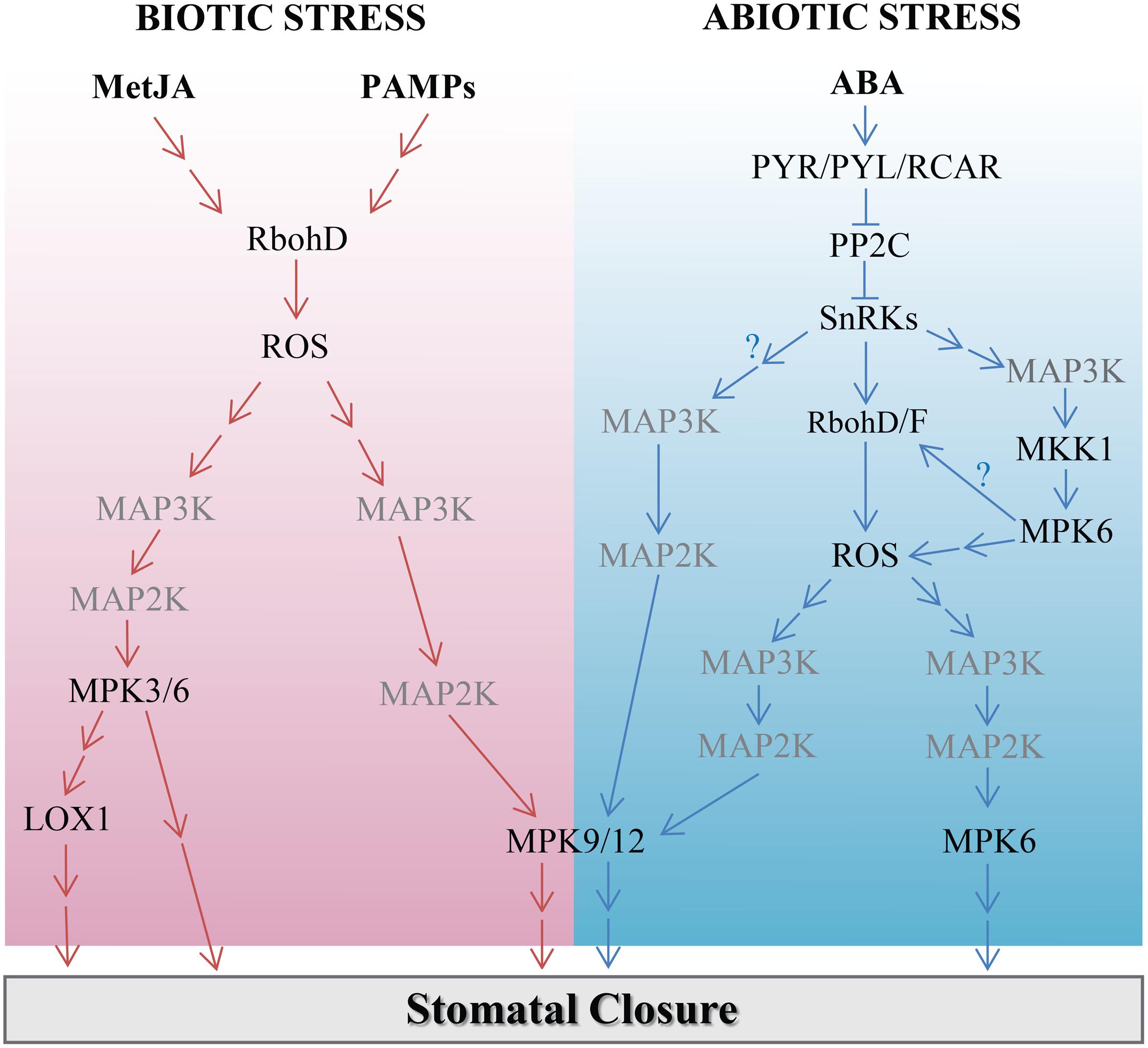
MAPK signaling pathway Biology Diagrams The MAPK family has been studied extensively; however, the role of these kinases in cell growth and cell-cycle control has become increasingly complex. Patterns have begun to emerge from these studies that show the functions of MAPK subfamilies at different stages of the cell cycle.
At least three MAPK families have been characterized: extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), Jun kinase (JNK/SAPK) and p38 MAPK. The above effects are fulfilled by regulation of cell cycle engine and other cell proliferation related proteins. The BCL2 family forms a protein-protein interaction network divided into anti-apoptotic and pro-apoptotic members, and the balance of binding between these two sides determines cell survival. Here, we discuss the intersections among the p38 MAPK, cell cycle, and apoptosis signaling pathways. Here we focus on the MAP kinase cascade and discuss the molecular mechanisms by which these extensively studied signaling pathways influence cell growth and proliferation.—Wilkinson, M. G., Millar, J. B. A. Control of the eukaryotic cell cycle by MAP kinase signaling pathways. FASEB J. 14, 2147-2157 (2000)

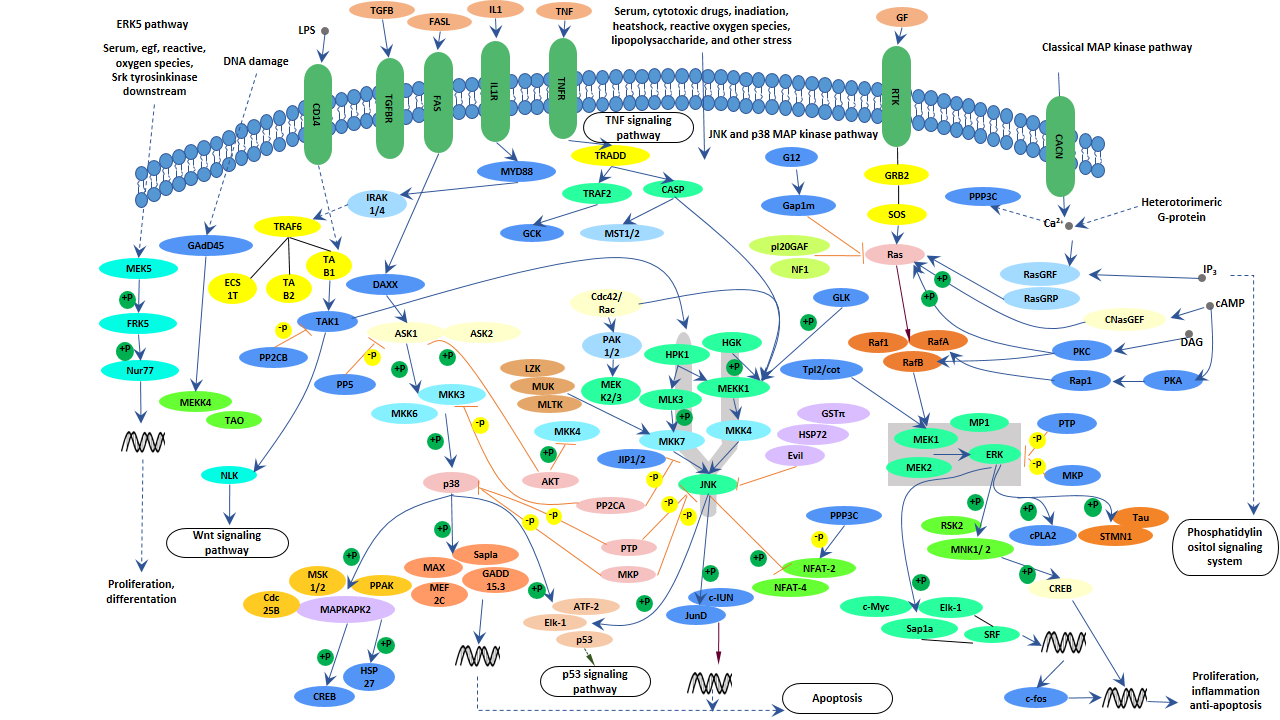
Activation and Function of the MAPKs and Their Substrates, the MAPK ... Biology Diagrams
It was demonstrated that in PC-12 cells transient Ras/Raf signal induces cell proliferation whereas a sustained activation causes these cells to differentiate and slowly ceased the cell cycle 11 The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family of kinases connects extracellular stimuli with diverse cellular responses ranging from activation or suppression of gene expression to the regulation of cell mortality, growth, and differentiation. The MAPK family has been studied extensively; however, the role of these kinases in cell growth and cell-cycle control has become increasingly Like pheromone stimulation, hyperosmotic stress also causes MAPK-mediated cell cycle arrest [201, 202]. Although this arrest is only transient, it seems important for osmoresistance. Unlike pheromone-imposed arrest, osmostress leads to cell cycle delays in both G1 and G2 [203, 204] . Presumably stress responses are most efficiently and safely

With regard to cell fate, the STE MAP3Ks drive cell-cycle arrest and survival, thereby promoting unicellular fitness. However, the TKL MAP3Ks promote cell-cycle progression or apoptosis. Taken together, it is tempting to speculate that the evolution of the MAPK signaling network played an important role in the unicellular to multicellular Cell cycle arrest upon cytoskeletal disruption is characterized by a failure to downregulate the cell cycle inhibitor p27 KIP1, to induce sustained p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation and activation, and to induce expression of D-type cyclins, which together with cdk4/6 are essential factors for promoting G1/S-phase Phosphorylation of Cdc25C by pp90Rsk contributes to a G(2) cell cycle arrest in Xenopus cycling egg extracts. Cell Cycle 4. 64. Chung, J., C. J. Kuo, G. R. Crabtree, and J. Blenis. 1992. Rapamycin-FKBP specifically blocks growth-dependent activation of and signaling by the 70 kd S6 protein kinases. Cell 69:1227-1236.