Mitotic perturbation is a key mechanism of action of decitabine in Biology Diagrams Based on their mechanism of action, anti-tumor drugs that target the cell cycle can be generally divided into three categories, namely, blocking DNA synthesis, causing DNA damage, and disrupting mitotic processes. In terms of mitotic inhibitors, most compounds used in the clinic impair the normal fu …

Current microtubule-targeting agents (MTAs) remain amongst the most important antimitotic drugs used against a broad range of malignancies. By perturbing spindle assembly, MTAs activate the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), which induces mitotic arrest and subsequent apoptosis. However, besides tox …
Mitotic inhibitor Biology Diagrams
Highly selective inhibitors developed against these targets showed robust cytotoxic activity in preclinical models. Similar to MT poisons, these anti-mitotics cause drug-specific and dose-dependent mitotic phenotypes through disruption of mitotic spindle morphology and MT-chromosome attachment or impairment of SAC (figure, bottom).

Though the concept of tyrosinase activated pro-drugs has permeated the drug delivery literature for quite some time [141-143], it has yet to be applied to the delivery of mitotic kinase inhibitors. There are two themes notable in the tyrosinase pro-drug development field: attachment to DNA-damaging agents [ 142 , 144 ] and dormant compounds A mitotic inhibitor is a substance that can impede cell cycle progression by preventing the entry into mitosis or inducing abnormal entry, leading to prolonged mitotic arrest and cell death, often used in cancer therapy to destroy proliferating cells. Drugs that are mitotic inhibitors impair this process by disrupting the equilibrium Secondary or acquired resistance is a result of drug treatment . Lallena MJ, de Dios A. Cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015;25:3420-3435. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.05.100. cells undergo mitotic arrest and since the compound disrupts spindle formation and

List of Mitotic inhibitors Biology Diagrams
Mitosis inhibitors in anticancer therapy: When blocking the exit becomes a solution. Author links open overlay panel Ana C. Henriques a b 1, Diana Ribeiro a c 1, underlying its potential as a drug target to delay mitotic slippage [150]. The Fcp1 phosphatase dephosphorylates the kinase Wee-1, which in turn dampens Cdk1 activation, Komlodi-Pasztor et al also recently highlighted this misconception (that tumor cells divide more frequently and more rapidly) as the downfall for mitotic agents. 58 Within the treatment duration, mitosis-specific drugs target only the cells in M-phase, leaving the rest of the G1- or S-phase tumor cells refractory to the cytotoxic effect. 59

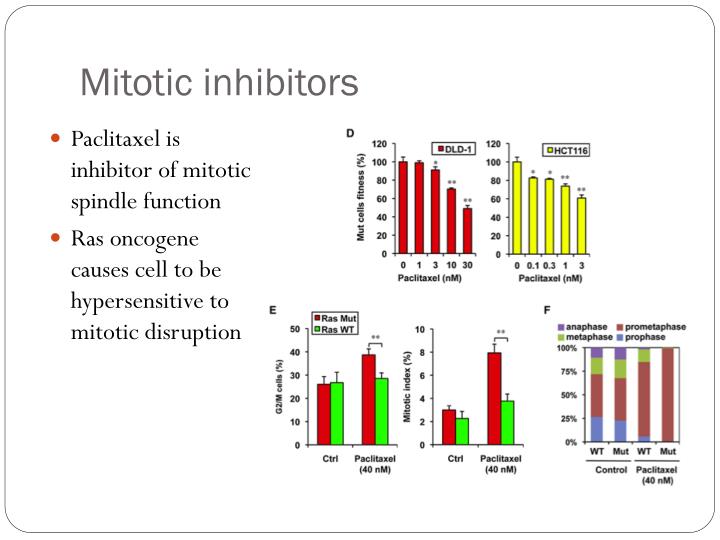
The structure of paclitaxel, a widely used mitotic inhibitor.. A mitotic inhibitor, microtubule inhibitor, or tubulin inhibitor, is a drug that inhibits mitosis, or cell division, and is used in treating cancer, gout, and nail fungus.These drugs disrupt microtubules, which are structures that pull the chromosomes apart when a cell divides. Mitotic inhibitors are used in cancer treatment

