Muscular System Anatomy and Physiology Biology Diagrams Learn about the anatomy and function of the muscles of the upper limb, divided into six regions: pectoral, shoulder, upper arm, forearm, and hand. See diagrams, videos, and quizzes to test your knowledge. Learn about the different muscles in your upper arm and forearm, and how they help you move your arms, hands and fingers. Find out about common conditions and disorders that affect your arm muscles, such as strains and rhabdomyolysis.

The part below the elbow joint is referred to as the 'lower' arm or forearm. So, the 5 muscles in the upper arm are counted as the arm muscles. Names & Anatomy of the 'Upper' Arm Muscles. The upper arm is divided into two compartments, the anterior (the front and inner side) and the posterior (the back and outer side). The group of 5 Learn about the main skeletal muscles of the arms, such as the biceps and triceps, and how they perform various functions and movements. Find out how to avoid injuries, such as strains and tendonitis, and how to keep your arm muscles stretched and strong. Learn about the five muscles of the arm, their origins, insertions, innervations and actions. The arm muscles are divided into anterior and posterior compartments, with the biceps brachii, coracobrachialis, brachialis, triceps brachii and anconeus.
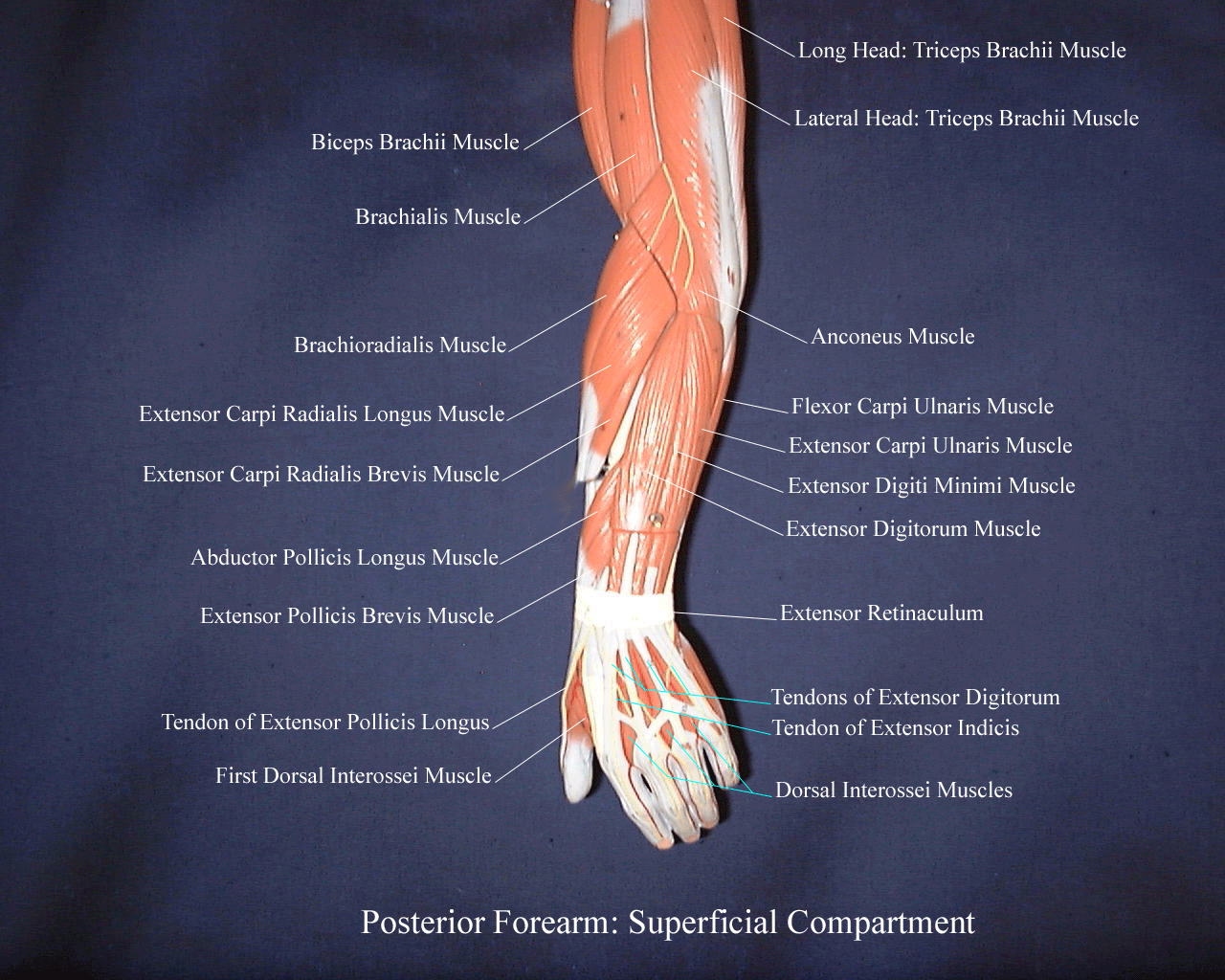
Arm Muscle Anatomy and Function Biology Diagrams
Learn about the anatomy of the four muscles of the upper arm - biceps, brachialis, coracobrachialis and triceps. See their attachments, innervation, function and clinical relevance with images and quiz. The arm muscle diagram comprises the brachialis, brachioradialis, triceps brachii, and biceps brachii.These muscles are in charge of pronation, supination, and wrist flexion/extension in addition to movements at the forearm and wrist joints. The diagram of arm muscles labeled illustrates the various muscles present in the arm, helping to understand their structure and function in movement and Learn about the 24 muscles of the arm, their location, structure, and function. Find out how arm muscles control movement at the elbow, forearm, wrist, and fingers, and what conditions can affect them.

Upper Arm Muscles. The upper arm extends from the shoulder to the elbow and contains two compartments: the anterior and the posterior. 1. Anterior Compartment: This compartment is located in front of the humerus, the main bone of the upper arm. It includes: - Biceps Brachii: This muscle has two heads that start at the front and back of the

