PDF Structure of the proteasome Biology Diagrams In mitosis, centromeric RNAs are known to stimulate Aurora B activity, which is essential for proper chromosome segregation [15, 17]. Hence, we demonstrated that the proteasome has an important role in α‐Sat regulation during G2/M and that its influence on the cell cycle is not limited to the ubiquitin‐dependent degradation of proteins.

The interaction between Rpn3 and Rpn5 connects these two clusters, implying a hierarchy in the incorporation of Rpn subunits into the lid complex. 117) Recently, it was proposed that the 20S proteasome functions as an assembly factor for the RP due to aberrant RP formation in the presence of defective 20S proteasomes in yeast. 105) It was also The primary function of the proteasome is to degrade proteins (1). Proteasome substrates include signaling molecules, tumor suppressors, cell-cycle regulators, transcription factors, inhibitory molecules (whose degradation activate other proteins), and anti-apoptotic proteins (e.g., Bcl-2), among others (1). CDK1 activation downstream of PLK1 activity was delayed in S16A mutant cells, suggesting an important role of α5-S16 phosphorylation in regulating PLK1 and mitosis. These data have revealed an unappreciated function of "exo-proteasome" phosphorylation of a proteasome subunit and may bring new insights to our understanding of cell cycle control.

Maintaining soluble protein homeostasis between nuclear ... Biology Diagrams
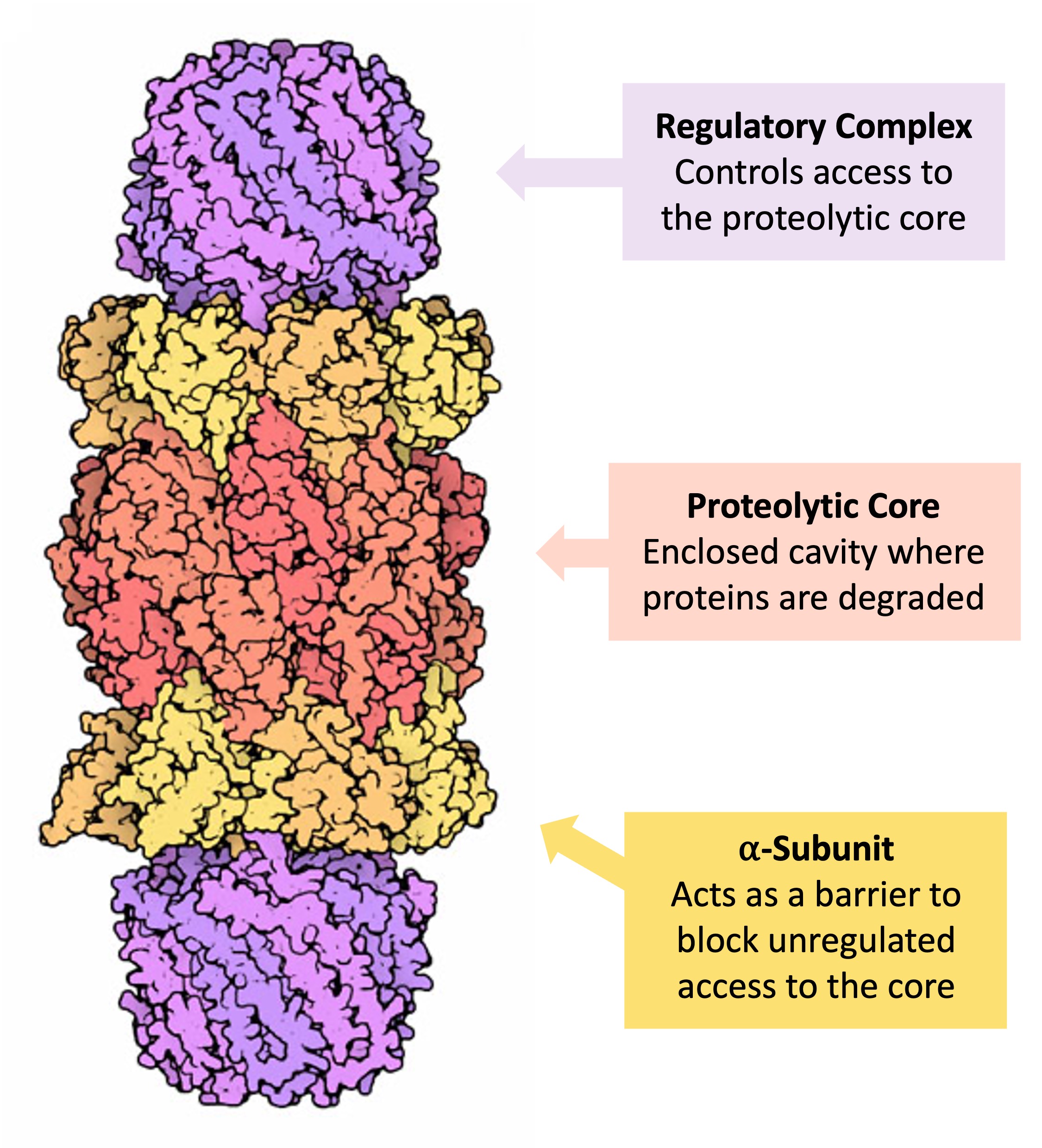
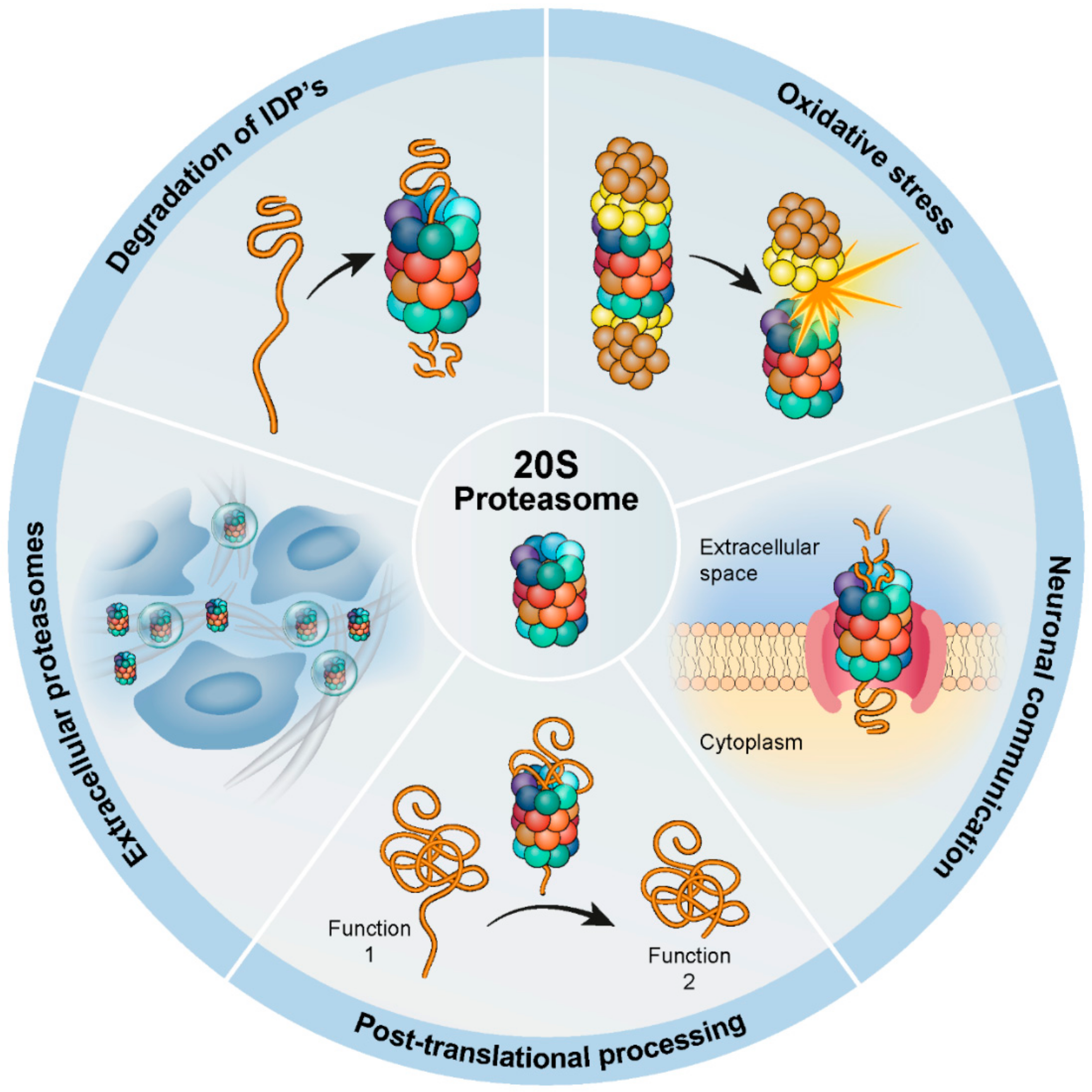
The above findings led to our prediction that S16-phosphorylated α5 functions outside the proteasome with other proteins to influence mitosis. Among dozens of proteins that were identified by IP/MS to selectively interact with phospho-α5, PLK1 stood out as one of the most abundant interacting proteins with a clearly defined role in mitosis. The proteasome subcomponents are often referred to by their Svedberg sedimentation coefficient (denoted S). The proteasome most exclusively used in mammals is the cytosolic 26S proteasome, which is about 2000 kilodaltons (kDa) in molecular mass containing one 20S protein subunit and two 19S regulatory cap subunits. The core is hollow and ated and uncontrolled mitosis, characteristic of cancer development and spread (2). Inhibition of the proteasome may therefore arrest or retard can-cer progression by interfering with the ordered degradation of cell-cycle proteins. Indeed, the inhi-bition of proteasome function results in pro-grammed cell death (apoptosis) (3-9). Preclinical
Throughout mitosis the proteasome remained predominantly at the nuclear periphery. During meiosis the proteasome was found to undergo dramatic changes in its localization. Throughout the first meiotic division, the signal is more dispersed over the nucleus. Tanaka K, Tsurumi C. The 26S proteasome: subunits and functions. Mol Biol Rep. 1997 Fulcher et al. show that MDM2 times mitosis through self-catalysed ubiquitination and proteasomal destruction, triggering G1 arrest following delays in mitosis associated with chromosome