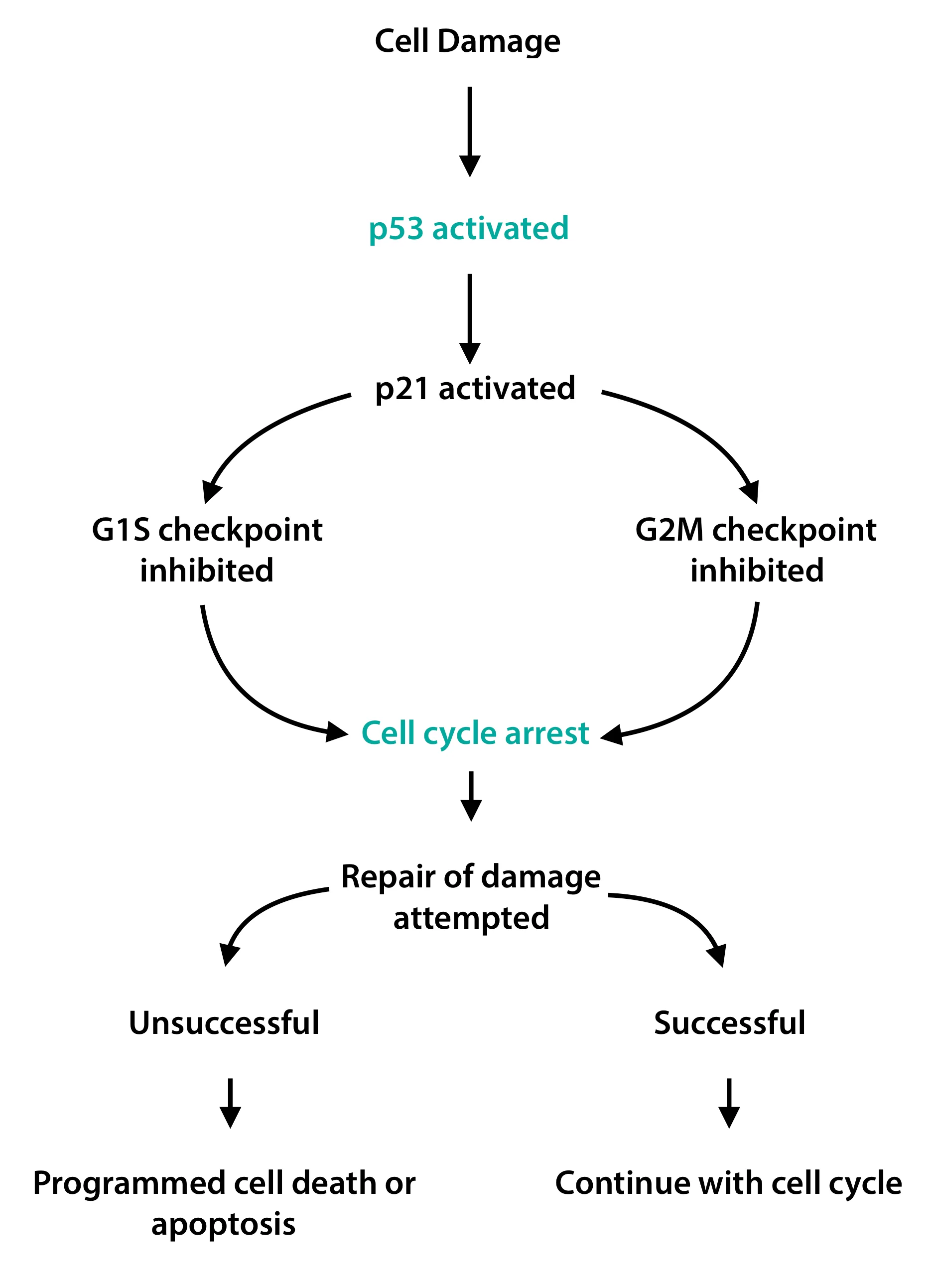
Policeman of the Cell cycle Firstclass Biology Diagrams Activated p53 promotes cell cycle arrest to allow DNA repair and/or apoptosis to prevent the propagation of cells with serious DNA damage through the transactivation of its target genes implicated in the induction of cell cycle arrest and/or apoptosis. Thus, the DNA-binding activity of p53 is tightly linked to its tumor suppressive function.
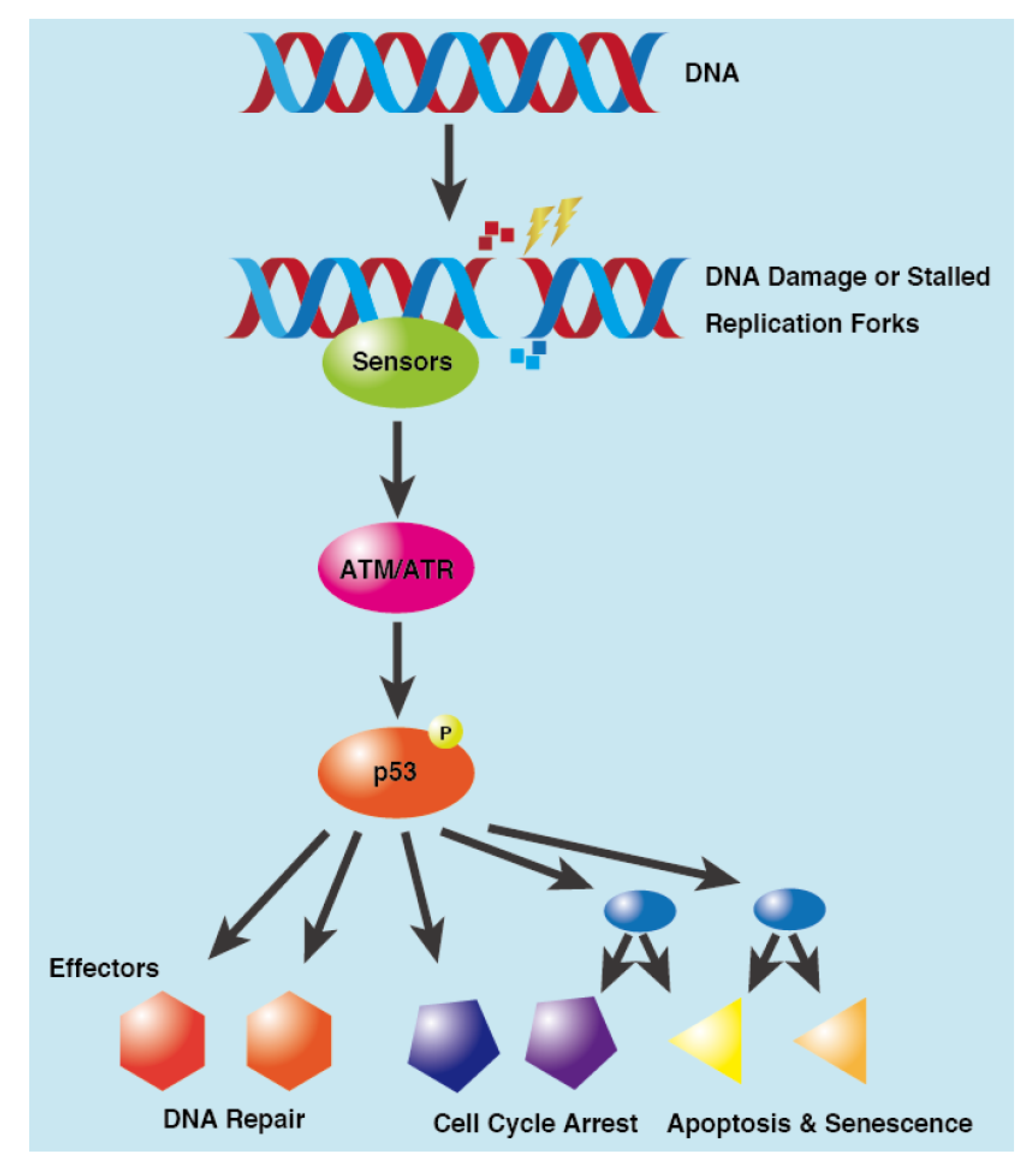
The tumor suppressor gene p53, implicated in diverse types of human tumors, functions both as a gene-specific transcription factor as well as a specific inhibitor of the transcription of certain genes: The two physiological outcomes of re-expression of wild type p53 in tumor cells, not expressing wild type p53, are G 1 arrest and apoptosis. The mechanism of G 1 arrest by p53 is much better The p53 transcription factor plays a critical role in cellular responses to stress. Its activation in response to DNA damage leads to cell growth arrest, allowing for DNA repair, or directs cellular senescence or apoptosis, thereby maintaining genome integrity. Senescence is a permanent cell-cycle a …
Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Functions of p53 in Tumor ... Biology Diagrams
The tumor suppressor p53 can induce cell cycle arrest. Induction of p53 leads to transcriptional downregulation of many cell cycle genes. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21/WAF1/CIP1/CDKN1A
Although several p53 target genes are activated upon cell cycle arrest induction, CDKN1A is the main induced gene in p53-mediated cell cycle arrest. The CDKN1A gene codes for the p21WAF1 protein, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 that can directly interact and inhibit CDK complexes resulting in cell cycle arrest [92, 93]. Through the Bulk p53 acetylation increased following DNA damage, and acetylated p53 was enriched at the promoter of the cell cycle arrest gene CDKN1A 70, yet mutating five 70 or six 127 acetylation sites in

Cell cycle regulation: p53 Biology Diagrams
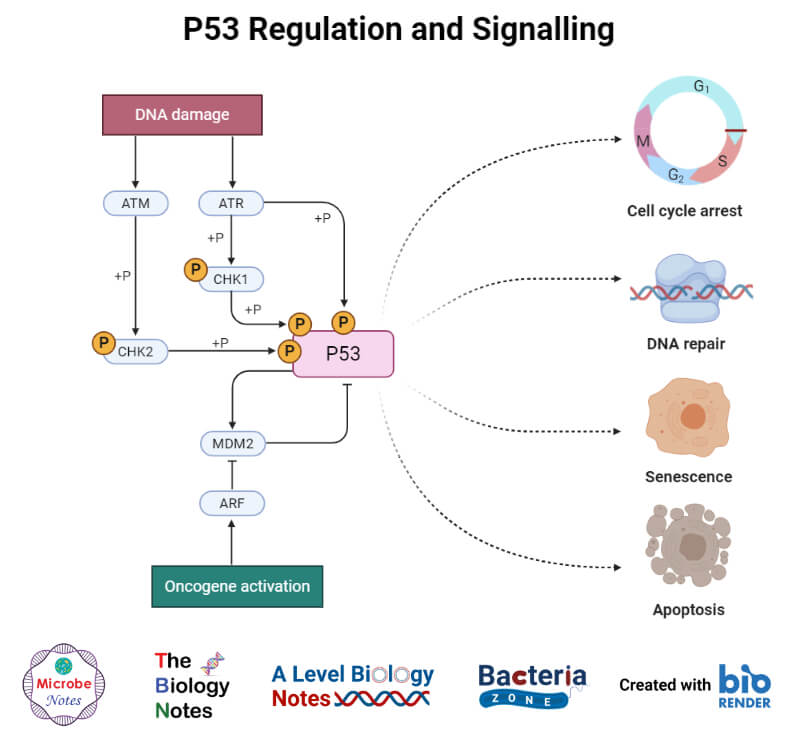
The p53 tumor suppressor protein plays a key role in the regulation of the cell cycle and cell death. The p53 protein is also involved in cell differentiation, DNA repair, senescence and angiogenesis.1-8 Wild-type (wt) p53 and intact signaling pathways are essential for the prevention of cancer, consistent with a high tumor incidence observed in p53 null mice9 and in p53-heterozygous Li P53 is a transcription factor highly inducible by many stress signals such as DNA damage, oncogene activation, and nutrient deprivation. Cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis are the most prominent outcomes of p53 activation. Many studies showed that p53 cell-cycle and apoptosis functions are important fo …
Cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis are the most noticeable biological outcomes of p53 activation in cell culture and animal experiments. The seminal finding of p53 as an inhibitor of oncogene-mediated transformation in foci formation is likely the result of its cell-cycle arrest or apoptosis activities (Finlay et al. 1989).The mammalian p53 DNA-binding domain has marginal thermostability, which

