Portrait of eurasian lynx in the forest at early winter Stock Photo Biology Diagrams Habitat fragmentation can isolate populations, making it difficult for animals to find food, mates, or new territories. This can lead to decreased biodiversity, affecting the overall health of the ecosystem. Climate change is another critical concern, as rising global temperatures can alter the taiga's cold climate. This article delves into the Maine lynx's physical traits, hunting techniques, reproductive behavior, and remarkable cold climate adaptations. Physical Characteristics. The Maine lynx, scientifically known as Lynx canadensis, is a medium-sized feline distinguished by its striking physical features.

The snowshoe hare and the Canadian lynx in the boreal forests of North America show 9- to 11-year density cycles. These are generally assumed to be linked to each other because lynx are specialist predators on hares. Based on time series data for hare and lynx, we show that the dominant dimensional structure of the hare series appears to be three whereas that of the lynx is two.

Environment and Climate Change - Gov Biology Diagrams
The taiga biome food web is a complex network of interactions between various organisms, from the smallest microorganisms to the largest apex predators. Every living being plays a crucial role in maintaining the ecosystem's delicate balance in this frozen wilderness. For instance, coniferous trees provide food for insects, which birds eat. These birds may, in turn, be prayed upon by larger

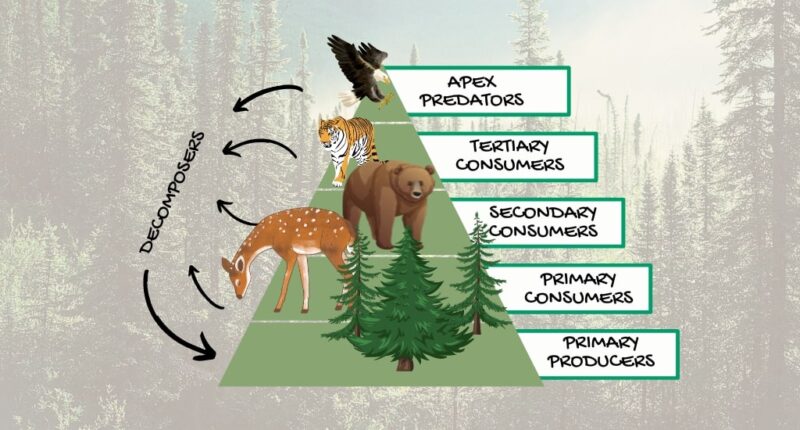
The cold climate and permafrost restrict the variety of plants, favoring hardy species like coniferous trees (spruce, pine, and fir) with adaptations like needle-like leaves to conserve water. Food Chain Dynamics. The wolf and lynx, as primary predators, maintain the population balance of herbivores such as moose and hares. Ecosystem Snowshoe hare is the primary food of the lynx. The population cycles of these two species are closely linked. When hares are plentiful, lynx eat little else and take about two hares every three days. Lynx prey upon mice, voles, squirrels, grouse, ptarmigan and carrion when hares are scarce. These food sources often do not meet the lynx's nutritional needs. The isolation of certain populations makes it difficult for animals to find food, mates, and new territories. This leads to decreased biodiversity, affecting the food web. Climate change; The global rise in temperature is altering the taiga's cold climate. This can lead to changes in plant and animal pollution, disrupting the food web. Pollution

Food web in taiga Biology Diagrams
Polar bears are the top of the Arctic's land-based food chain. Their biggest threat to survival is not other species. Rather it is the changing environmental conditions brought on by climate A taiga biome food web shows the feeding relationships and how energy flows between organisms at different trophic levels. 1. Producers: It mainly consists of coniferous trees like spruce, fir, and pine. These trees are well adapted to the cold climate, with needle-like leaves that reduce water loss through transpiration. 2. Taiga Biome Food Chain. Various types of plants form the foundation of food chain in the taiga biome. The main trophic levels in the taiga biome food chain are producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers and decomposers. Read on, to know about these taiga biome nutritional levels in detail.